Что такое биткоин?
Биткоин - это цифровая форма денег, но в отличие от обычных фиатных валют, к которым мы все так привыкли, он не находятся под контролем центрального банка. Вместо этого, основа управления финансовой системой биткоина – это тысячи компьютеров, распределенных по всему миру. Любой может принять участие в работе данной экосистемы после установки определенного программного обеспечения с открытым исходным кодом.
Биткоин был первой криптовалютой, анонс которой состоялся в 2008 (и запуск в 2009 году). Он предоставляет пользователям возможность отправлять и получать цифровые деньги (биткоины, b в нижнем регистре или BTC). Но основное качество, которое делает данную валюту такой привлекательной, так это то, что её нельзя подвергнуть цензуре, средства нельзя расходовать более одного раза, а транзакции можно совершать в любое время и из любого места.
Зачем пользоваться биткоином?
Люди используют биткоин по ряду причин. Многие ценят первую криптовалюту за её инклюзивный характер (от англ. permissionless), т.е. любой у кого есть подключение к интернету, может отправлять и получать эти монеты. Это чем то похоже на наличные деньги, по причине того, что никто не может помешать вам использовать их, и такое преимущество данных средств в цифровой среде означает, что с помощью биткоина вы можете обмениваться валютой по всему миру.
Что делает биткоин ценным?
Биткоин является децентрализованным, устойчивым к цензуры, безопасным и безграничным.
Последнее качество сделало его крайне привлекательным для таких случаев использования, как международные денежные переводы и платежи (римесса), при условии нежелания пользователя раскрывать свои личные данные (как в случае с использованием дебетовой или кредитной карты).
Вместо того, чтобы тратить свои биткоины, многие предпочитают хранить их на длительный срок (также известно как ходлинг). Биткоин получил прозвище «цифровое золото» из-за ограниченного количества доступных монет. Некоторые инвесторы рассматривают биткоин как средство сбережения. Причиной этому послужило наличие таких факторов как: дефицит и сложность производства, его также часто сравнивают с драгоценными металлами, такими как золото или серебро.
Холдеры считают, что наличие этих качеств в сочетании с глобальной доступностью и высокой ликвидностью делают его идеальным средством для сохранения богатства в течение длительных периодов. Они считают, что ценность биткоина со временем только продолжает расти.
Как работает биткоин?
Когда Алиса создает транзакцию Бобу, она не отправляет средства так, как вы того ожидаете. Это не имеет ничего общего с цифровым эквивалентом передачи ему долларовой банкноты. Это больше похоже на то, что Алиса пишет на листе бумаги (который всем доступен для ознакомления), что она передает Бобу свой доллар. Когда Боб отправляет те же средства Кэрол, она может увидеть, что у Боба есть деньги, просмотрев операции записанные на листе.
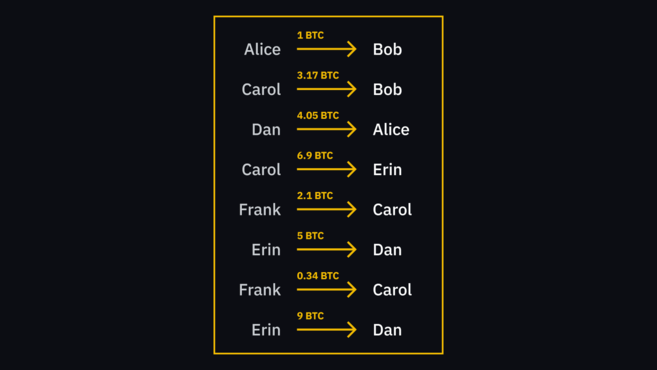
Этот лист представляет собой особый вид базы данных и его название в системе биткоина – блокчейн. Все участники сети имеют в наличии копии такой базы, которые хранятся на их устройствах, а также они постоянно контактируют друг с другом для синхронизации новой информации.
Когда пользователь совершает платеж, он транслирует его напрямую в одноранговую сеть (от англ. peer-to-peer network), которая не является централизованным банком или учреждением по обработке денежных переводов. Чтобы добавить новую информацию, блокчейн биткоина использует специальный механизм, под названием майнинг. Именно благодаря этому процессу новые блоки транзакций фиксируются в виде записей в блокчейне.
Что такое блокчейн?
Блокчейн - это регистр или главная бухгалтерская книга, которая предназначена исключительно для добавления информации. После того, как данные были записаны в такую книгу их практически невозможно изменить или удалить. Блокчейн обеспечивает это путем наличия указателя на предыдущий блок, в каждом последующем блоке.
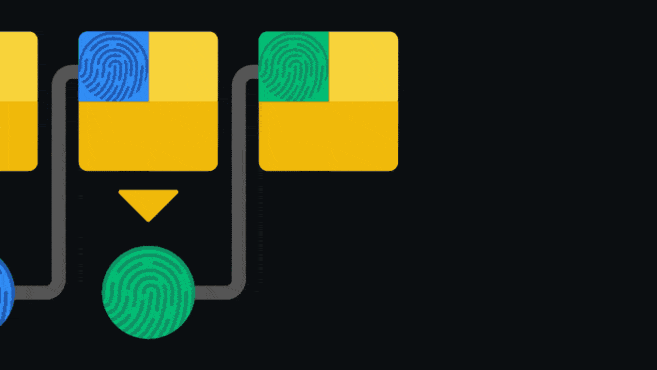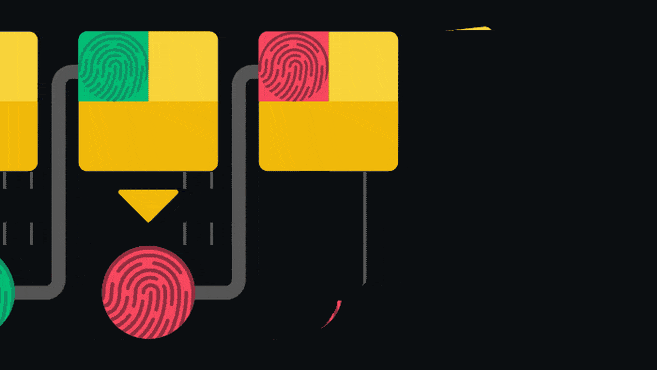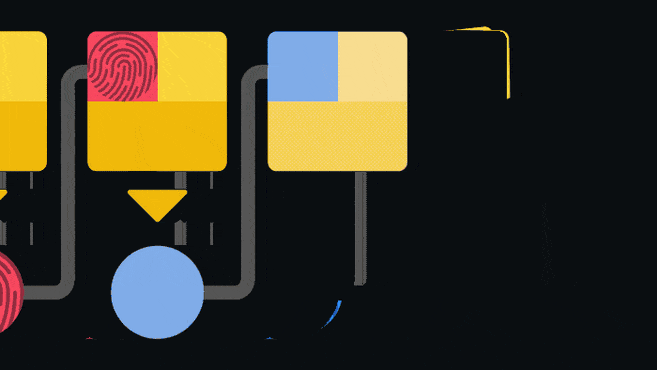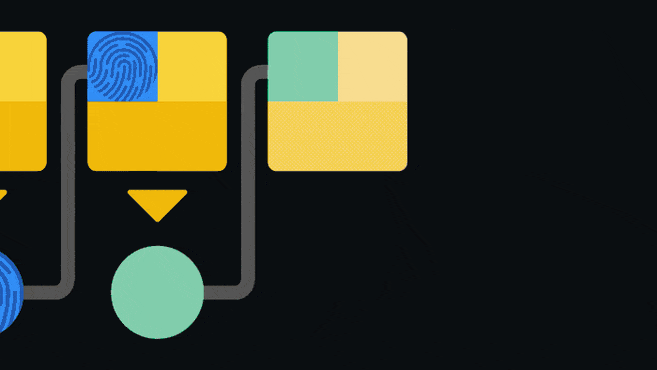
Данный указатель является так называемым хешем предыдущего блока. Хеширование включает в себя пропускание информации через одностороннюю функцию для получения уникального отпечатка входных данных. Если входные данные будут подвержены даже самым мельчайшим изменениям, их отпечаток станет совершенно другим. Поскольку длина цепочки из взаимосвязанных блоков постоянно увеличивается, у пользователей отсутствует возможность изменения старой записи, по причине того, что для этого необходимо будет признать статус недействительности для всех последующих блоков. Такая структура является одним из основных компонентов, который обеспечивает безопасность блокчейн-сети.
Мы рекомендуем вам ознакомится с нашим введение в работу блокчейн-систем. Cм. статью: «Блокчейн-технологии. Руководство для начинающих».
Является ли биткоин легальным?
Биткоин является совершенно легальным в большинстве стран мира. Однако есть несколько исключений, по причине которых, вам в обязательном порядке необходимо ознакомится с юрисдикцией вашего государства в отношении цифровых валют, прежде чем инвестировать в неё.
В странах, где такой вид денег закреплен на законодательном уровне, государственные органы применяют к ним различные регулирующие подходы в виде налогообложения и правил пользования. Нормативно-правовая база в целом все еще недостаточно развита и скорее всего изменится в ближайшие годы.
История биткоина
Кто создал биткоин?
Создателя первой криптовалюты никто не знает! Человек, который разработал биткоин использовал псевдоним Сатоши Накамото, но точная информация об этой личности полностью отсутствует. Сатоши может быть одним человеком или группой разработчиков в любой точке мира. Имя имеет японское происхождение, но уровень владение английским языком заставил многих поверить в то, что он, она или они из англоязычной страны.
Именно Сатоши опубликовал вайтпейпер биткоина и его программное обеспечение, но затем он исчез в 2010 году.
Является ли Сатоши первооткрывателем технологии блокчейн?
К моменту своего появления, биткоин сочетал в себе ряд технологий, которые уже являлись существующими. Концепция цепочки из блоков не появилась вместе с биткоином. Зарождение подобной неизменяемой структуры данных можно проследить от начала 90-х годов, когда Стюарт Хабер и У. Скотт Сторнетта предложили систему создания штампов времени для цифровых документов. По аналогии с сегодняшними блокчейнами, они использовали криптографические методы для защиты данных и защиты от подделки информации.
Интересный факт: в вайтпейпере Сатоши не используется термин “блокчейн”.
См. также: «История блокчейн».
Цифровая валюта до биткоина
Биткоин был не первым в своем роде, но он является наиболее успешной попыткой реализации цифровых денежных средств. Тем не менее, предыдущие попытки предоставили Сатоши возможность для изобретения такой системы:
DigiCash
DigiCash – это компания, которую основал криптограф и ученый в области информационных технологий Дэвид Чаум в конце 1980-х годов. Она была представлена в качестве решения ориентированного на конфиденциальность онлайн-транзакций на основе статьи, автором которой является сам Чаум.
Модель DigiCash представляла собой централизованную систему, но тем не менее, это был довольно интересный эксперимент. Позже компания обанкротилась, что по мнению Чаума было связано с началом их работы, до того, как электронная коммерция действительно взлетела.
B-money
Система B-money первоначально была описана в предложении, опубликованном в 1990-х годах компьютерным инженером Вэй Даем. Он был процитирован в вайтпейпере биткоина, и это понятно почему. В B-money была предложена система, под названием Proof of Work (используемая в майнинге биткоина) и использование распределенной базы данных, где пользователи смогут подписывать свои транзакции. Во второй версии b-money также описана идея, похожая на стейкинг, которая сегодня используется в других криптовалютах.
В конечном счете B-money так и не взлетели, поскольку проект не смог выйти за рамки чернового варианта. Тем не менее, биткоин явно черпал свое вдохновение из концепций, которые предоставил Дай.
Bit Gold
Сходства между Bit Gold и Bitcoin настолько велики, что некоторые считают, что Ник Сабо это и есть Сатоши Накамото. В своей основе, Bit Gold состоит из регистра, в котором записываются строки с данными, полученными в результате работы алгоритма Proof of Work.
Как и B-money, данная монета не получила никакого развития в дальнейшем. Однако сходство Bit Gold с биткоином закрепило за ним титул «предшественника биткоина».
Откуда появляются новые биткоины?
Как создаются новые монеты?
Биткоин имеет ограниченное предложение и еще не все монеты находятся в циркуляции. Единственный способ создать новые монеты, это процесс, под названием майнинг – специальный механизм добавления данных в блокчейн.
Какое количество биткоинов уже добыто?
Протокол фиксирует максимальное предложение биткоина в количестве двадцати одного миллиона монет. По состоянию на 2020 год было добыто чуть менее 90%, но для производства оставшихся биткоинов потребуется более ста лет. Это связано с периодическим событием под названием халвинг, задача которого состоит в том, чтобы постепенно уменьшать вознаграждение за майнинг.
Как работает майнинг биткоина?
Майнинг позволяет участникам добавлять блоки в блокчейн. Для этого они должны направить вычислительную мощность своего компьютера для решения определенной криптографической головоломки. В качестве стимула присутствует вознаграждение, доступное любому, кто найдет соответствующее решение и сформирует действительный (валидный) блок.
Для того, чтобы сформировать блок необходимо большое количество ресурсов, в то время как очень просто проверить его действительность. Если кто-то попытается обмануть сеть и добавить недействительный блок, такой запрос будет немедленно отклонен, и майнер не получить оплату за майнинг.
Награда, которую зачастую именуют, как вознаграждение за блок состоит из двух компонентов: комиссии, связанные с транзакциями, и субсидия за блок. Блочная субсидия является единственным источником «свежих» биткоинов. С каждым добытым блоком добавляется единица в общее предложение монет.
Сколько времени занимает майнинг одного блока?
Протокол корректирует сложность майнинга так, чтобы поиск решения для нового блока занимал приблизительно десять минут. Блоки не всегда майнятся ровно десять минут, данная установка является своеобразным ориентиром для всех участников сети.
Как начать пользоваться биткоином
Как купить биткоин?
Как купить биткоин с помощью кредитной/дебетовой карты
Binance позволяет вам без проблем покупать биткоины через ваш браузер. Для этого вам необходимо выполнить следующие действия:
- Перейдите в раздел: «Купить и продать криптовалюту».
- Выберите криптовалюту, которую вы хотите купить, и валюту, в которой будете совершать оплату.
- Войдите на Binance или зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет своего аккаунта.
- Выберите способ оплаты.
- При необходимости введите данные своей карты и подтвердите свою личность.
- На этом всё! Ваш биткоин вскоре будет зачислен на ваш Binance-аккаунт.
Как купить биткоин на P2P-рынке
Вы также можете покупать и продавать биткоин на P2P-рынке. Это позволяет вам покупать монеты у других пользователей напрямую с мобильного приложения Binance. Для этого вам нужно будет:
- Запустить приложение, пройти процесс регистрации, если у вас нет своего аккаунта и войти в систему.
- Выберите «Покупка и продажа в один клик», а затем нажмите на вкладку «Купить» в левом верхнем углу интерфейса.
- Вам будет предложено несколько различных вариантов оплаты, нажмите «Купить» напротив того, который вы хотите использовать.
- Также вы можете осуществить платеж с помощью других криптовалют (вкладка Купить крипто) или фиатной валютой (вкладка Купить фиат).
- Ниже вас попросят указать способ оплаты. Выберите тот, который вам больше всего подходит.
- Выберите Купить BTC.
- Теперь вы должны совершить платеж. После того, как оплата будет проведена, нажмите Отметить как оплаченное, а затем подтвердите операцию.
- Сделка завершается, когда продавец отправляет вам монеты.
Что можно купить пользуясь биткоином?
Есть много вещей, которые вы можете купить с помощью биткоина. На сегодняшний день у вас могут возникнуть некоторые трудности при попытке найти продавцов, которые официально принимают биткоины, в качестве средства оплаты в обычных физических магазинах. Однако вы можете найти множество веб-сайтов, которые принимают первую криптовалюту или позволяют покупать подарочные карты с ее помощью для получения других видов услуг.
Вот лишь некоторые из вещей и услуг, которые вы можете купить используя биткоин:
- Билеты на самолет
- Аренда гостиничных номеров
- Недвижимость
- Еда и напитки
- Одежда
- Подарочные сертификаты
- Онлайн подписки
Где можно расплачиваться биткоином?
Вы можете потратить биткоин в огромном количестве мест, и с каждым днем их становится все больше! Давайте рассмотрим некоторые из них.
Сэкономьте на больших комиссиях кредитной карты в своих путешествиях по миру! Вы можете забронировать авиабилеты и отели с помощью биткоина и других криптовалют благодаря TravelbyBit. Регистрируйтесь и бронируйте перечисленные услуги в криптовалюте и получите 10% скидку.
Spendabit - это поисковая система товаров, которые вы можете купить с помощью биткоина. Просто найдите то, что вы хотели бы купить, и получите список продавцов, у которых вы можете купить это с помощью биткоина.
Поисковик всех криптовалютных мерчантов и банкоматов в вашем районе. Если вы хотите потратить свой биткоин и просто ищете подходящих магазин для этого, то данный ресурс может стать для вас идеальным вариантом.
Благодаря данному сервису вы можете приобрести подарочные сертификаты для несколько сотен различных услуг и даже пополнить свой телефон с помощью биткоина и других криптовалют. Это довольно легко сделать, наряду с тем, что для вас доступна возможность провести операцию на Lightning Network для оплаты своих покупок.
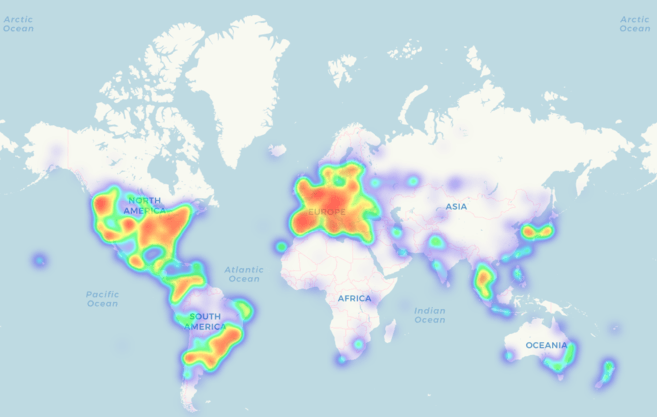 Тепловая карта ритейлеров, которые принимают криптовалюту в качестве средства для оплаты. Источник: https://coinmap.org/
Тепловая карта ритейлеров, которые принимают криптовалюту в качестве средства для оплаты. Источник: https://coinmap.org/
Что случится, если я потеряю свои биткоины?
Поскольку банк никоим образом не взаимодействует с такими операциями, исключительно вы несете ответственность за сохранность своих сбережений. Некоторые предпочитают хранить криптовалюту на биржах, в то время как другие склоняются к использованию различных кошельков. Если для вас предпочтительнее пользоваться кошельком, вам обязательно следует записать свою сид-фразу, чтобы в случае чего, всегда была возможность восстановить доступ к своему кошельку.
Возможно ли отменить биткоин-транзакцию?
После того, как данные добавлены в блокчейн, их будет не просто изъять и удалить (на практике, это практически невозможно реализовать). Это означает, что когда вы совершаете транзакцию, ее нельзя будет отменить. Вы всегда должны дважды, а лучше трижды проверять, что вы отправляете свои средства на правильный адрес. Пример того, как чисто теоретически можно реверсировать транзакцию, см. Что такое атака 51%?
Могу ли я зарабатывать деньги на биткоине?
Вы можете как заработать деньги на биткоине, так и потерять их. В основном, долгосрочные инвесторы покупают и холдят биткоин, предполагая, что в будущем он подорожает. Другие предпочитают активно торговать им в паре с другими криптовалютами, чтобы получать прибыль в краткосрочной и среднесрочной перспективе. Обе эти стратегии довольно рисковые, но зачастую так складывается, что они являются более эффективными, нежели подходы с низким уровнем риска.
Некоторые инвесторы предпочитают использовать гибридную стратегию. Они холдят биткоины в качестве долгосрочных инвестиций, одновременно торгуя некоторыми торговыми парами (в отдельном портфеле) в краткосрочной перспективе. Не существует правильного или неправильного способа распределения активов в вашем портфеле, поскольку у каждого инвестора свой аппетит к риску и финансовые цели.
Лендинг становится все более популярной формой пассивного дохода. На основе предоставления своих монет кому-то другому, вы можете получить определенный процент, который будет поступать вам на счет. Такие платформы, как Binance Lending, позволяют вам воспользоваться такой возможностью заработка на биткоине и других криптовалютах.
Как правильно хранить свои биткоины?
Существует множество вариантов хранения монет, каждый из которых имеет свои сильные и слабые стороны.
Хранение биткоина на Binance
Кастодиальное решение относится к такому типу хранения, когда пользователь не лично владеет монетами, а доверяет это третьему лицу. Чтобы совершать транзакции, для начала необходимо зайти на платформу третьей стороны. Биржи, такие как Binance, часто используют эту модель, поскольку она гораздо более эффективная и удобная для торговли.
Хранение ваших монет на Binance позволяет легко получить доступ к торговым операциям или лендингу.
Хранение ваших монет на биткоин-кошельке
Решения, не связанные с ограничением свободного перемещения активов, являются полной противоположностью предыдущего типа хранения, по той причине, что они предоставляют пользователю контроль над своими средствами. Для данного вида, вы используете то, что называется кошелек. Кошелек не является местом хранения ваших монет, такие варианты только содержат криптографические ключи, которые дают доступ к активам на блокчейне. Всего существует два основных типа кошельков:
Горячие кошельки
Горячий кошелек - это программное обеспечение на вашем устройстве, в форме мобильного или десктоп приложение, обязательным условием которого является постоянная необходимость интернет-соединения для того, чтобы легко отправлять и получать монеты. Простой в использовании мобильный кошелек с поддержкой множества монет – это Trust Wallet. Поскольку горячие кошельки функционируют на основе постоянного подключения к интернету, они являются более удобными в использовании для отправки различных платежей, но в свою очередь такие решения более уязвимы для хакерских атак.
Холодные кошельки
Криптовалютные кошельки, которые не подвержены влиянию со стороны интернета, называют холодными кошельками. Они намного устойчивее к хакерским атакам, по причине отсутствия векторов атаки в режиме онлайн, но следовательно, имеют тенденцию предоставлять менее удобный пользовательский опыт. Примером могут послужить аппаратные или бумажные кошельки.
Если вы хотите больше подробностей на данную тему, мы рекомендуем вам ознакомится с нашей статьей: «Виды кошельков для хранения криптовалюты».
Халвинг биткоина
Что такое халвинг биткоина?
Халвинг биткоинов (иногда упоминается как халвенинг биткоина) – это просто событие, которое уменьшает вознаграждение за блок. Как только происходит халвинг, награда, которую получают майнеры за валидацию новых блоков, делится надвое (после халвинга майнеры получают только половину того, что раньше). Тем не менее, это не влияет на комиссии за транзакцию.
Как это работает?
Когда только запустили биткоин, майнеры получали по 50 BTC за каждую валидацию блока.
Первый халвинг произошел 28 ноября 2012 года. В этот момент протокол сократил субсидию блока с 50 BTC до 25 BTC. Второй халвинг состоялся 9 июля 2016 (с 25 BTC до 12.5 BTC). Следующий, в мае 2020 года, снизил награду до 6.25 BTC.
Вы можете проследить определенную закономерность. Обращая внимание на даты, халвинг происходит каждые 4 года. Хоть это и является предусмотренным событием, протокол не предполагает установку каких-либо конкретных дат. Вместо этого время халвинга определяется высотой блока, таким образом, халвинг происходит каждые 210 000 блоков. На основе данной информации, мы можем ожидать, что субсидия сократится вдвое через 2 100 000 минут (помните, что добыча блока занимает ~ 10 минут).
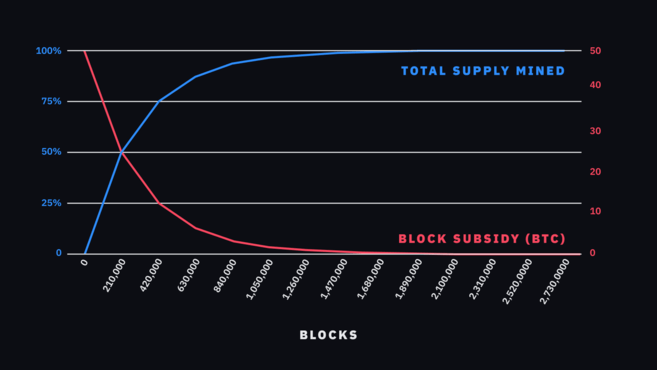
На данном графике, мы видим уменьшение блочной субсидии с течением времени и ее взаимосвязь с общим предложением. Вам может показаться, что сумма награды упала до нуля, а максимальное предложение уже циркулирует на рынке, но это не так, по той причине, что кривые расположены невероятно близко друг к другу. Ожидается что субсидия достигнет нуля приблизительно в 2140 году.
Почему это происходит?
Этот процесс является одной из основных особенностей биткоина, которую Сатоши Накамото так и не успел объяснить, также как и то, почему он ограничил общее предложение в количестве двадцати одного миллиона единиц. Некоторые предполагают, что это не более чем обычный финансовый продукт, стартовавший с субсидирования блока в размере 50 BTC, которое уменьшается вдвое каждые 210 000 блоков.
Наличие ограниченного предложения означает, что валюта не будет склонна к обесцениванию в долгосрочной перспективе. Это резко контрастирует её с фиатными деньгами, которые со временем теряют свою покупательную способность, когда в обращении появляются новые единицы.
Также имеет смысл в ограничении скорости, с которой участники могут добывать монеты. Следует учесть тот факт, что 50% было сгенерировано блоком на высоте 210 000 (т.е. к 2012 году). Если бы субсидия оставалась на одном и том же уровне, все единицы были бы добыты к 2016 году.
Механизм работы халвинга обеспечивает экономический стимул на более чем 100 лет. Благодаря этому, системе биткоина предоставляется достаточное количество времени, чтобы привлечь пользователей, в целях развития внутреннего рынка комиссионных сборов за валидацию операций.
На что влияет халвинг?
Те, кто больше всего страдает от халвинга, так это майнеры. Это связано с тем, что блочная субсидия составляет значительную часть их дохода. Когда происходит халвинг, майнеры начинают получать только половину своей награды за аналогичное количество работы. Также их вознаграждение состоит из комиссионных сборов за транзакции, но на сегодняшний день, эта сумма составляет лишь часть награды за блок.
Таким образом, халвинги могут сделать майнинг невыгодным для отдельной категории участников. Пока что не известно как это может повлиять, на всю индустрию в целом. Тем не менее, сокращение вознаграждений за блок может привести к дальнейшей централизации майнинг-пулов или просто поспособствовать развитию более эффективной реализации майнинга.
Если биткоин в дальнейшем будет полагаться на алгоритм Proof of Work, то для поддержания прибыльности майнинга необходимо будет увеличить стоимость комиссии. Такой сценарий вполне возможен, если блоки начнут включать в себя больше транзакций. В случае большого количества транзакций в режиме ожидания, в первую очередь в обработку пойдут транзакции с более высокой комиссией.
Исторически складывается так, что резкий рост стоимости биткоина сопровождается с халвингом. Данных об этом не так уж и много, поскольку это происходило только два раза. Многие связывают такое ценовое движение с дефицитом биткоинов на рынке и сокращением притока новых монет вдвое.
Другая часть пользователей не согласна с этим, утверждая, что новость о халвинге уже отразилась на рынке (см. детали в гипотезе эффективного рынка). Также часто упоминается о том, что прошлый бурный рост частично связан с тем, что отрасль была чрезвычайно слабо развита в период первых двух халфингов. В настоящее время рынок стал намного популярнее, предлагая сложные торговые инструменты, тем самым располагая к участию более широкий круг инвесторов.
Когда следующий халвинг биткоина?
Следующий халвинг ожидается в мае 2024 года, после этого вознаграждение за добычу блока упадет до 6.25 BTC. Следите обратным отсчетом до халвинга биткоина на Binance Academy.
Распространенные заблуждения о биткоине
Является ли биткоин анонимной валютой?
Если ответить кратко, то нет. Поначалу биткоин может показаться анонимным, но это в корне неправильное утверждение. Блокчейн биткоина является общедоступным, и любой может ознакомится со всеми транзакциями в сети. Ваша личность не привязана к адресам вашего кошелька в блокчейне, но сторонний зритель, располагающий необходимыми ресурсами потенциально может связать их вместе. Точнее было бы утверждение, что биткоин является псевдоананимной валютой. Биткоин-адреса видны всем, а имена их владельцев – нет.
Тем не менее, система является относительно приватной, и существуют методы, которые еще больше затруднят сторонним зрителям процесс определения движений ваших биткоинов. Свободно доступные технологии могут создать правдоподобное отрицание, чтобы «разорвать связь» между адресами. Более того, будущие обновления могут значительно повысить приватность, в качестве примера см. «Введение в конфиденциальные транзакции».
Биткоин - это скам?
Ответ: нет. Также, как и бумажные деньги, биткоин может быть использован в незаконной деятельности, но это не делает его скамом.
Биткоин – это цифровая валюта, у которой отсутствует единый контролирующий орган. Недоброжелатели называют его пирамидальной схемой, но он изначально не соответствует определению. Такой вид цифровой валюты функционирует одинаковым образом вне зависимости от того, сколько он стоит, 20$ или 20 000$ за одну монету. Биткоину более десяти лет и данная технология уже доказала свою безопасность и надежность.
К сожалению, биткоин используется во многих мошенничествах, о которых вам следует знать. Они могут включать в себя фишинг и другие схемы социальной инженерии, такие как фейковые гивэвеи и аирдропы. Возьмите себе за правило: «если это звучит слишком хорошо, чтобы быть правдой, это вероятнее всего мошенничество». Никогда и никому не передавайте свои приватные ключи или сид-фразу, и будьте осторожны с махинациями, которые предлагают преумножить количество вашей валюты с небольшим риском с вашей стороны. Если вы отправите свои монеты мошеннику или на фейк-гивэвей, вы их потеряете навсегда.
Является ли биткоин пузырем?
В период резких параболических повышений цены биткоина появилось множество людей, считающих, что это спекулятивный пузырь. Многие сравнивали биткоин в эти периоды с тюльпаноманией или пузырем доткомов.
В связи с уникальной природой биткоина, как цифрового децентрализованного продукта, его цена полностью определяется спекуляциями на свободном рынке. Таким образом, существует множество факторов, влияющих на цену биткоина, в конечном счете они и определяют спрос и предложение на рынке. Так как предложение биткоина ограничено и выпуск монет происходит по строгому графику, предполагается, что в долгосрочной перспективе спрос превысит предложение.
Также криптовалютные рынки относительно малы по сравнению с традиционными. Это означает, что биткоин и другие криптоактивы имеют тенденцию быть более волатильными, и довольно часто можно наблюдать краткосрочный дисбаланс между предложением и спросом.
Другими словами, иногда биткоин может быть волатильным активом. Но волатильность – это часть финансовых рынков, особенно тех, у которых сравнительно низкие объем и ликвидность.
Используется ли в биткоине шифрование?
Ответ: Нет. Это распространенное заблуждение, поскольку блокчейн биткоина не использует шифрование. Каждому пиру сети необходимо иметь возможность читать транзакции, чтобы удостовериться, что они валидны. Вместо этого используются цифровые подписи и хеш-функции. Несмотря на то, что некоторые алгоритмы цифровых подписей используют шифрование, к биткоину это не относится.
Тем не менее, стоит отметить, что многие приложения и криптовалютные кошельки используют шифрование для дополнительной защиты пользовательских кошельков с паролем. Такие методы шифрования не имеют ничего общего с блокчейном, они просто интегрированы в технологии, которые задействуют его.
Масштабируемость биткоина
Что такое масштабируемость?
Масштабируемость является мерой способности системы развиваться в соответствии с растущим спросом. Если вы размещаете веб-сайт, заполненный запросами, вы можете масштабировать его, добавив больше серверов. Если вы хотите запускать более интенсивные приложения на вашем компьютере, вы можете обновить его компоненты.
В контексте криптовалют, мы используем этот термин для простого описания обновления блокчейн-сети в целях увеличения возможного количества обрабатываемых транзакций.
Почему масштабируемость необходима для биткоина?
Для правильного и стабильного функционирования в качестве ежедневного платежного решения биткоин должен быть быстрой валютой. В текущем виде он имеет относительно низкую пропускную способность, это в свою очередь означает, что каждый блок может обработать ограниченное количество транзакций.
Как вы уже знаете из предыдущей главы, майнеры получают часть вознаграждения за блок в виде комиссий за транзакции. Пользователи прикрепляют их к своим транзакциям, чтобы стимулировать майнеров добавить операцию в блокчейн.
В свою очередь, майнеры стремятся окупить вложения в оборудование и электроэнергию, поэтому они отдают предпочтение транзакциям с более высокой комиссией. Если в «комнате ожидания» сети (называемый mempool) большое количество транзакций, сумма комиссии может значительно возрасти, поскольку пользователи хотят быстрее сделать перевод. В самом худшем случае средняя сумма комиссии составляла более 50$.
Какое количество транзакций может обрабатываться в сети биткоина?
Основываясь на среднем количестве транзакций в блоке, биткоин в настоящий момент может обрабатывать примерно пять транзакций в секунду. Это намного ниже, чем у централизованных платежных решений, и это является одной из основных издержек использования децентрализованной валюты.
Поскольку биткоин не находится под управлением центра по обработке данных, принадлежащему одному юридическому лицу, биткоин-сеть должна самостоятельно лимитировать размер своих блоков. Можно интегрировать новый размер блока, который позволит реализовывать до 10 000 транзакций в секунду, но это может повредить децентрализацию сети. Помните, что полные ноды должны загружать новую информацию примерно каждые десять минут. Если это станет слишком обременительно для них, они вероятнее всего перейдут в автономный режим.
Если протокол будет использоваться для подобных платежей, биткоин-энтузиасты считают, что эффективное масштабирование может быть достигнуто другими различными способами.
Что такое Lightning Network?
Lightning Network – это предложение для решения проблем с масштабируемостью биткоина. Мы называем это решением второго уровня, по причине построения транзакций за рамками основного блокчейна. Вместо записи всех транзакций на базовом уровне они обрабатываются другим протоколом, построенным поверх него.
Lightning Network предоставляет пользователям возможность бесплатно и практически мгновенно отправлять средства, при этом нет никаких ограничений на пропускную способность (при условии, что пользователи имеют возможность как отправлять валюту, так и получать ее). Чтобы использовать биткоин в сети Lightning Network два участника блокируют свои монеты на специальном адресе. Такой адрес обладает уникальным свойством, он реализует биткоины только в случае согласия обеих сторон.
Из этого адреса стороны ведут приватный регистр операций, который может перераспределять балансы, не передавая информацию об этом в основную цепь. Они публикуют транзакцию в блокчейне по завершению всех необходимых переводов, и после этого протокол обновляет балансы кошельков. Обратите внимание, что всем участникам нет необходимости доверять друг другу. Если кто-то попытается смухлевать, протокол быстро идентифицирует и пресечет любую мошенническую деятельность.
В целом, подобный платежный канал требует от пользователя наличие двух транзакций в цепочке, одна для пополнения своего адреса и другая для последующего распределения монет. Это означает, что в этот временной промежуток участники канала могут осуществить тысячи переводов. С дальнейшим развитием и оптимизацией технологии это может стать критически важным компонентом для больших блокчейн-систем.
Для более подробного описания проблем связанных с масштабируемостью и их потенциальные решения см. статью «Масштабируемость блокчейна – сайдчейны и платежные каналы».
Что такое форк?
Поскольку биткоин с открытым исходным кодом, любой может модифицировать его программное обеспечение. Вы можете добавить новые правила или удалить старые, чтобы удовлетворить различные потребности. Однако не все изменения являются равноправными: некоторые обновления сделают ваш узел несовместимым с сетью, в то время как другие будут обратно совместимы.
Софтфорк
Софтфорк – это изменение правил, которое позволяет обновленным узлам взаимодействовать со старыми. Давайте возьмем в качестве примера размер блока. Предположим, что у нас есть размер блока 2 МБ и только половина сети решила принять обновление, после которого все блоки не должны превышать 1 МБ. Теперь обновленные ноды отвергают блоки, превышающие допустимый размер.
Старые ноды все еще могут принимать такие блоки или распространять свои. Это означает, что все ноды остаются частью одной сети, независимо от того, какую версию они используют.
В анимации представленной ниже мы можем видеть, что 1 МБ блоки принимаются как старыми, так и обновленными нодами. Однако более новые узлы не будут распознавать блоки размером 2 МБ, поскольку они уже следуют новым правилам.

Обновление биткоина под названием Segregated Witness (или SegWit) является одним из примеров софтфорка. Благодаря грамотному использованию технологии, оно представило новый формат для блоков и транзакций. Старые ноды по-прежнему продолжают получать блоки, но они не могут осуществлять валидацию нового типа транзакций.
Хардфорк
В свою очередь, хардфорк является более разрушительным. Предположим, что половина сети хочет увеличить размер блока с 2 МБ до 3 МБ. Если вы попытаетесь отправить блок с размером 3 МБ не обновленным нодам, они отклонят его, поскольку в правилах четко указано, что максимальный размер, который они могут принять, составляет 2 МБ. Поскольку две сети больше не совместимы, блокчейн распадается на две отдельных сети.

Черная цепь на диаграмме представленной выше является оригинальной. Блок 2 – это место, где произошел хардфорк. После форка обновленные ноды начали производить более крупные блоки (зеленые). Старые ноды не распознают их, поэтому они продолжат идти по другому пути. В последствии такого события появилось два блокчейна, которых объединяет общая история транзакций до блока 2.
Теперь есть два разных протокола, и каждый cо своей валютой. Вся информация полностью дублируется в новой сети, это означает, что если у вас было 20 BTC в исходной цепочке, то у вас также появится 20 NewBTC в новой.
В 2017 году биткоин пережил довольно противоречивый хардфорк по аналогичному сценарию. Меньшинство участников хотели увеличить размер блока, чтобы обеспечить более высокую пропускную способность и уменьшить комиссионные сборы. Остальные участники сети считали, что это довольно плохая стратегия масштабирования. В конце концов, хардфорк породил Bitcoin Cash (BCH), который отделился от сети биткоина и теперь имеет свое независимое сообщество и дорожную карту.
Чтобы узнать больше о форках см. статью: «Хардфорки и софтфорки».
Участие в работе сети биткоина
Что такое нода биткоина?
Нода биткоина – это термин, используемый для описания программы, которая является своеобразным мостом для взаимодействия пользовательского оборудования с сетью биткоина. Это может быть что угодно, от мобильного телефона, с которого осуществляется управление биткоин-кошельком, до отдельного компьютера, на котором хранится полная копия записей блокчейн-сети.
Существует несколько типов нод (узлов сети), каждый из которых выполняет определенные функции. Все они выступают в роли конечной точки связи с сетью, основная задача которых – своевременно передавать информацию о транзакциях и блоках.
Как работает нода биткоина?
Полные ноды
Полная нода осуществляет валидацию (проверку) транзакций и блоков на наличие соблюдения определенных требований сети (т.е. следуют правилам). Большинство полных нод используют программное обеспечение, под названием Bitcoin Core, которое является эталонной реализацией биткоин-протокола.
Bitcoin Core – это программа, созданная Сатоши Накамото в 2009 году, в то время она называлась просто биткоин, но позже была переименована, чтобы избежать путаницы. Также можно использовать другие реализации подобного ПО, при условии, что они будут совместимы с Bitcoin Core.
Полные ноды являются неотъемлемой частью децентрализованной среды биткоина. Они скачивают и проверяют блоки и транзакции, после чего распространяют информацию о проделанной работе остальной части сети. Поскольку они независимо проверяют подлинность информации, которую им предоставляют, пользователь ни в чем не полагается на третью сторону.
Если полная нода хранит полную копию блокчейн-сети, такой источник данных называется архивом полной ноды. Однако некоторые пользователи отказываются от хранения информации о старых блоках, чтобы сэкономить место, по причине того, что блокчейн биткоина содержит более 200 ГБ данных о транзакциях.
 Карта расположения полных нод биткоина. Источник: bitnodes.earn.com
Карта расположения полных нод биткоина. Источник: bitnodes.earn.com
Упрощенные ноды
Упрощенные ноды не так работоспособны и менее ресурсоемкие, в отличии от полных нод. Они позволяют пользователям взаимодействовать с сетью, но без выполнения всех операций, которые осуществляет полная нода.
Если полная нода скачивает все блоки для проверки, упрощенная нода загружает только часть каждого блока (так называемый заголовок блока). Хотя заголовок блока имеет крошечный размер, он содержит информацию, которая позволяет пользователям провести полную проверку транзакций в определенном блоке.
Упрощенные ноды идеально подходят для устройств с ограничениями в пропускном способности (полосе пропускания). Обычно такой тип нод используется в десктопных и мобильных кошельках. Однако они не могут осуществлять валидацию, тем самым упрощенные ноды находятся в зависимости от работы полных нод.
Майнинг-ноды
Майнинг-ноды - это полные ноды, которые помимо остальных задач, выполняют дополнительную – производство блоков. Как мы уже упоминали ранее, для этого им необходимо специальное оборудование и программное обеспечение, чтобы добавлять данные в блокчейн.
Майнинг-ноды рассматривают транзакции в пендинг статусе и хешируют их вместе с другой информацией для генерации определенного числа. Если это число падает ниже целевого значения, установленного протоколом, блок является валидным и его можно транслировать другим полным нодам.
Для того, чтобы добыть блок, не полагаясь на кого-то другого, майнеры вынуждены запускать полную ноду, в противном случае, они не смогут понять, какие транзакции нужно включить в блок.
Если участник сети хочет майнить, но не хочет запускать полную ноду, он может подключиться к серверу, который предоставит ему необходимую информацию. Если вы работаете в пуле (т.е. работаете вместе с другими), только один человек должен запустить полную ноду.
Детальнее про виды нод и их назначение см. статью «Что такое узлы (ноды)»?
Как запустить полную биткоин-ноду
Полная нода может быть полезна для разработчиков, продавцов и конечных пользователей. Запуск клиента Bitcoin Core на вашем оборудовании дает вам преимущества конфиденциальности и безопасности, а также укрепляет сеть биткоина в целом. С полной нодой вы больше не будете полагаться на кого-либо еще для прямого взаимодействия с экосистемой.
Несколько компаний ориентированных на биткоин предлагает пользователям своеобразные «play-and-play» ноды. Предварительно собранное оборудование поставляется потребителю, которому нужно только включить его, чтобы начать загрузку данных о блокчейне. Это может быть намного удобнее для менее технически осведомленных пользователей, но в основном такие решения значительно дороже, чем настройка своих собственных устройств.
В большинстве случаев для этого достаточно старого ПК или ноутбука. Не рекомендуется запускать ноду на вашем повседневном компьютерном устройстве, поскольку это может значительно замедлить его работу. Блокчейн непрерывно растет, поэтому вам нужно убедиться в том, что у вас достаточно свободного места на жестком диске для загрузки всей информации о сети.
Жесткого диска на 1 ТБ будет вполне достаточно на следующие несколько лет, при условии отсутствия каких-либо серьезных изменений в размере блока. Другие требования включают в себя 2 ГБ ОЗУ (по умолчанию, в основном у большинства компьютеров данный показатель выше необходимого) и высокую пропускную способность.
Рекомендуем ознакомится с подробным описанием процесса настройки запуска полной ноды на bitcoin.org.
Как майнить биткоин
В первые дни существования биткоина у первых пользователей была возможность создавать новые блоки с помощью обычного ноутбука. Поскольку система была неизвестная для многих, не много людей составляли конкуренцию в области майнинга. По причине очень низкой активности, протокол подстраивался и устанавливал низкую сложность майнинга.
Поскольку хешрейт сети быстро набирал обороты, участникам необходимо было обновлять свое оборудование, чтобы оставаться конкурентоспособными. Переходя на различные виды аппаратного обеспечения, отрасль майнинга в конечном итоге вступила в эпоху интегральных схем специального назначения (ASIC).
Как следует из названия, такие устройства создаются с одной единственной целью. Они чрезвычайно эффективны, но в рамках только одной задачи. Итак, майнинг ASIC – это специализированное компьютерное оборудование, которое используется исключительно для майнинга и ничего более. Биткоин-ASIC может майнить только биткоины, но не сможет добывать другие монеты, которые не используют аналогичный алгоритм.
На сегодняшний день, майнинг биткоина требует значительных инвестиций, не только в оборудование, но и в электроэнергию. На момент написания публикации хорошее устройство для майнинга осуществляет до десяти триллионов расчетных операций в секунду. В то время как «асики» очень эффективны, они потребляют огромное количество электроэнергии. Если у вас нет доступа к нескольким майнинговым установкам и дешевому электричеству, вы вряд ли сможете выйти в прибыль добывая биткоины.
Настройка своих устройств на майнинг довольно простая процедура, поскольку многие асики сразу поставляются с внутренним программным обеспечением. Самый популярный вариант – это направить свою майнинговую мощь в майнинг-пул, где вы будете вместе с другими участниками пытаться обнаружить и добыть блок. Если у вас получилось сделать это, вы получите часть вознаграждения за блок пропорционально вашему хешрейту.
Вы также можете майнить в одиночку, работая на себя. В таком случае, вероятность добычи блока будет намного ниже, но вы сохраните всю награду себе, если осуществите его валидацию.
Сколько времени занимает майнинг биткоина?
Трудно дать точный ответ, поскольку нужно учитывать несколько различных переменных. Скорость добычи монеты зависит от количества электричества и вашего хешрейта. Вам также необходимо учитывать затраты на работу и обслуживание устройств для майнинга. Чтобы получить представление о доходах, получаемых от майнинга биткоинов, рекомендуется использовать специальный калькулятор майнинга для оценки сопутствующих затрат.
Кто может вносить изменения в код биткоина?
Программное обеспечение Bitcoin Core имеет открытый исходный код, поэтому каждый может внести свой вклад в развитие системы биткоина. Благодаря этому у вас есть доступ к новым функциям, которые будут добавлены к более чем 70 000 строк кода, а также возможность предложить свои нововведения. Вы также можете сообщать об ошибках, переводить и улучшать вид документации.
Изменения в программном обеспечении проходят строгий процесс проверки. Все это для того, чтобы в программе, которая обрабатывает операции ценностью в сотни миллиардов долларов не было каких-либо уязвимостей.
Если вы заинтересованы в том, чтобы внести свой вклад в биткоин, обязательно ознакомьтесь с подробностями на сайте Bitcoin Core либо с публикацией в блоге Джимми Сонга, в которой он описывает свой опыт участия в этом.