Введение
Криптовалюты обладают несколькими уникальными свойствами: их не получится легко взломать или отключить, и любой человек может использовать их для передачи средств по всему миру без каких-либо посредников.
Сохранность этих функций гарантируется определенными компромиссами: поскольку за работу криптовалютной сети отвечает множество нод, пропускная способность в ней ограничена. Из-за этого число транзакций в секунду (TPS), которое может обработать сеть блокчейна, является относительно низким для технологии, которая стремится к массовому распространению.
Чтобы преодолеть эти ограничения и увеличить пропускную способность сети, был предложен ряд решений по масштабируемости. В этой статье мы рассмотрим одно из расширений протокола Биткоина — Lightning Network.
Что такое Lightning Network?
Lightning Network — это сеть, развернутая поверх блокчейна для обеспечения быстрых одноранговых (P2P) транзакций. Это решение доступно не только для Биткоина: другие криптовалюты, например Litecoin, тоже могут его интегрировать.
Что значит «развернутая поверх блокчейна»? Lightning Network — это офчейн-решение, или же решение второго уровня. Оно позволяет совершать переводы без необходимости записывать каждую транзакцию в блокчейне. Сеть Lightning Network отделена от сети Биткоина: она имеет собственные ноды и программное обеспечение, но все еще должна обмениваться данными с основным чейном. Чтобы войти или выйти из Lightning Network, необходимо создать особые транзакции на блокчейне.
То, что происходит с вашей первой транзакцией, это создание своего рода смарт-контракта с другим пользователем. Вскоре мы разберемся со всеми деталями. Пока что представьте смарт-контракт, формирующий приватный регистр с другим пользователем. В данном регистре вы можете записать множество транзакций, и они будут видны только вам и вашему напарнику, но никто из вас не сможет обмануть систему из-за некоторых специфических особенностей.
Этот мини-регистр называется каналом. Скажем, Алиса и Боб внесли по 5 BTC на смарт-контракт. Баланс на их канале составляет по 5 BTC у каждого. Затем Алиса может ввести в регистр перевести 1 BTC Бобу. Теперь у Боба будет 6 BTC, а у Алисы — 4. Далее Боб отправляет Алисе 2 BTC, обновляя балансы до 6 BTC у Алисы и 4 BTC у Боба. Это может продолжаться некоторое время.
В любое время, любой из них может опубликовать текущее состояние канала в блокчейне. В этот момент остатки на каждой стороне канала распределятся между соответствующими сторонами в цепочке.
Транзакции в сети Lightning происходят молниеносно (само ее название означает молнию). Поскольку ждать подтверждения блока не нужно, платежи могут осуществляться с максимальной скоростью, которую поддерживает интернет-соединение.
В чем необходимость реализации Lightning Network?
На данный момент Lightning Network (LN) — это наиболее разумный подход к масштабированию блокчейна Биткоина. Координировать изменения в такой огромной экосистеме довольно сложно, так как существует риск возникновения хардфорков и потенциальных ошибок. По этим и другим причинам проводить какие-либо эксперименты в сети крайне опасно.
Если проводить подобные эксперименты за рамками блокчейна, можно получить гораздо более гибкие решения. В этом случае ошибки и сбои не повлияют на сеть Биткоина. Решения второго уровня не подрывают основы безопасности, на которых базируется работа протокола уже более 10 лет.
Также нет необходимости переходить от старого способа ведения дел. Ончейн-операции (внутри сети) продолжают работать в штатном режиме, для всех конечных пользователей, но помимо этого, также будет доступна возможность совершать операции на офчейне (за рамками сети).
Есть несколько преимуществ использования Lightning Network. Некоторые из основных мы рассмотрим ниже.
Масштабируемость
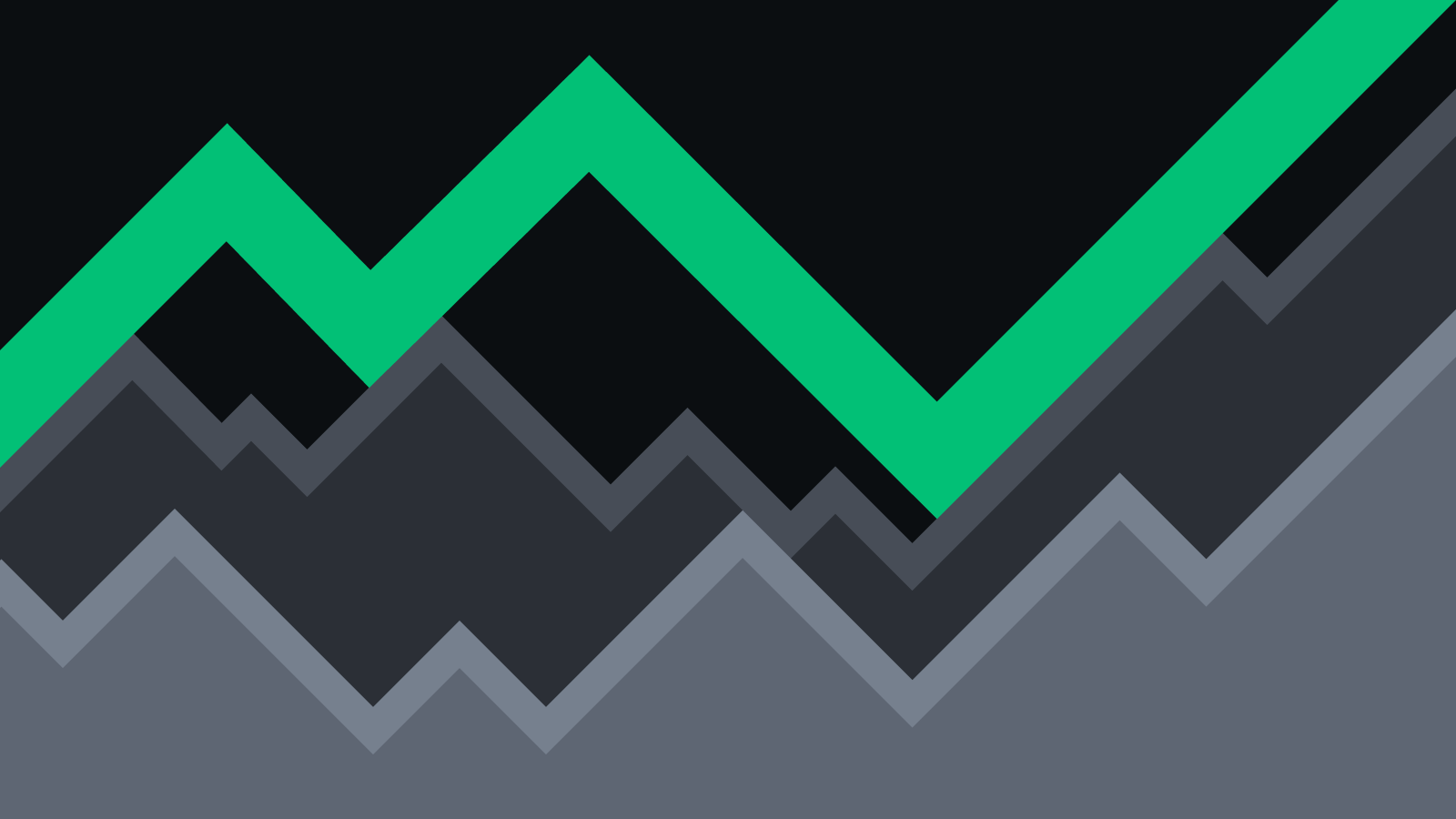
Блоки Биткоина создаются каждые десять минут и могут содержать определенное количество транзакций. Место внутри блока ограничено, поэтому пользователи делают ставки для продвижения своих транзакций вперед. Поскольку майнеров в первую очередь интересует доход, транзакции с наиболее высокой ставкой они обрабатывают в первую очередь.
Когда средства одновременно отправляет небольшое количество пользователей, это не проблема. При малой активности в следующий блок, скорее всего, будет включена даже транзакция с низкой комиссией. Но если переводы будет совершать множество людей, средний размер комиссии значительно вырастет. За всю историю комиссия несколько раз превышала $5, а на пике бычьего рынка в 2017 году она поднялась выше $50.

Средняя комиссия за транзакцию биткоина (в USD)
Это может показаться незначительным для транзакций размером в несколько тысяч долларов, но для небольших переводов это критический фактор. Кто захочет платить за кофе стоимостью 3$ при комиссии за перевод в 5$?
Благодаря Lightning Network вы по-прежнему оплачиваете две комиссии: одну за открытие канала, а другую за закрытие. Но вы и ваш контрагент получаете возможность абсолютно бесплатно совершать тысячи транзакций в рамках открытого канала. Когда вы закончите выполнение всех необходимых операций, вам просто нужно будет опубликовать финальное состояние ваших балансов в блокчейне.
В глобальном масштабе, чем больше пользователей будет полагаться на автономные решения, такие как Lightning Network, тем рациональнее станет использоваться место в блоке. Низкочастотные и высокочастотные переводы могут осуществляться в рамках платежных каналов, в то время как место в блоках будет использоваться для более крупных транзакций и открытий/закрытий таких каналов. Это сделает систему доступной для более широкой пользовательской базы и позволит масштабировать сеть в долгосрочной перспективе.
Микроплатежи
В Биткоине минимальный размер транзакции составляет 0,00000546 BTC — на момент написания статьи это около четырех центов. Это небольшая сумма, но в Lightning Network можно отправлять всего 0,00000001 BTC, то есть один сатоши.
Что касаемо микроплатежей, Lightning является наиболее жизнеспособным вариантом в этом контексте. Оплата комиссий за регулярные транзакции делает нецелесообразной отправку небольших сумм на основной цепочке, однако внутри канала, вы можете абсолютно бесплатно перемещать малые части биткоина.
Микроплатежи подходят для множества вариантов использования. Некоторые полагают, что они могли бы стать жизнеспособной заменой модели на основе подписей, где пользователи вместо этого платят небольшую сумму при каждом использовании данного сервиса.
Конфиденциальность
Второе преимущество Lightning Network — это высокая степень конфиденциальности пользователя. Сторонам не нужно публиковать информацию о своих каналах в сети. Блокчейну предоставляется лишь информация о том, что конкретная транзакция открыла канал, но подробности остаются неизвестными. Если участники делают свой канал приватным, то только они будут знать, какие транзакции осуществляются внутри него.
Если у Алисы есть канал с Бобом, а у Боба есть канал с Кэрол, Алиса и Кэрол могут отправлять средства друг другу через Боба. Если Дэн подключен к Кэрол, Алиса также получит возможность переводить средства и ему. Вы можете представить это в виде постоянно расширяющейся разветвленной сети взаимосвязанных платежных каналов. При такой настройке, вы не сможете быть уверены в том, кому Алиса отправила средства после закрытия канала.
Как это работает?
Итак, выше мы уже поверхностно рассмотрели как Lightning Network полагается на каналы между нодами. Давайте теперь рассмотрим принцип работы системы изнутри.
Адреса с мультиподписью
Адрес с мультиподписью предполагает использование нескольких приватных ключей для осуществления перевода. При его создании указывается количество приватных ключей, которые могут расходовать средства и необходимы для подписания транзакции. Например, схема 1 из 5 означает, что пять ключей могут создать валидную подпись, а для осуществления перевода требуется только один. Схема 2 из 3 будет означать, что из трех возможных ключей для перевода необходимы два.
Для создания Lightning-канала участники блокируют средства по схеме 2 из 2. Создать подпись могут только два приватных ключа, и они оба необходимы для перемещения монет. Рассмотрим это на примере Алисы и Боба. Они собираются совершать много переводов в ближайшие месяцы, поэтому создают канал в Lightning Network.
Это начинается с того, что оба они вносят, скажем, по 3 BTC каждый, на их общих адрес с мультиподписью. Стоит еще раз отметить, что Боб не может забрать средства с такого адреса без согласия Алисы или наоборот.
Это равносильно наличию листа бумаги, в котором регулируется баланс каждой стороны. Например, если они имеют стартовый баланс 3 BTC и Алиса хочет внести Бобу платеж размером в 1 BTC, почему бы просто не отметить, что Алиса теперь владеет 2 BTC, а Боб 4 BTC? Такие балансы можно отслеживать до тех пор, пока стороны не примут обоюдное решение: вывести средства.
Это возможно, но в чем может быть подвох? Что еще более важно, не является ли такая простота для кого-то поводом отказаться от сотрудничества? Если Алиса получает 6 BTC, а Боб ни одного, Боб ничего не теряет (кроме своих дружеских отношений с Алисой), отказываясь высвободить средства.
Hash Timelock Contracts (HTLC)
Вышеприведенная система проста и не предлагает богатый функционал, по сравнению с другими современными конфигурациями. Все становится намного интереснее, когда мы представляем механизм, который обеспечивает «контракт» между Алисой и Бобом, предполагающий возможность возврата средств из канала, в случае, если одна из сторон не захочет играть по правилам.
Такой механизм называется Hash Timelock Contract (HTLC). Его концепция довольно проста. Она объединяет две технологии — хеш-лок и тайм-лок — для предотвращения нежелательных действий в платежных каналах.
Хеш-лок — это условие для транзакции, при котором средства может расходовать только человек, которому известны определенные данные (секрет). Отправитель хеширует часть данных и включает хеш в транзакцию для получателя. Разблокировать средства можно, предоставив отправителю оригинальные данные (секрет), соответствующие заданному хешу.
Тайм-лок — это условие, которое не позволяет тратить средства раньше определенного времени. Временной период указывается в виде либо фактического времени, либо высоты блока.
HTLC создаются путем объединения хеш-локов и тайм-локов. На практике, HTLC могут использоваться для создания условных платежей: получатель должен предоставить секрет до определенного времени, или отправитель получает право на возврат средств. Следующую часть лучше всего будет рассмотреть на нашем популярном примере, поэтому давайте снова вернемся к Алисе и Бобу.
Открытие и закрытие каналов
Рассмотрим пример: Алиса и Боб только что создали транзакции, которые финансируют адрес с мультиподписью. Данный адрес они собираются использовать в ближайшее время, но пока эти транзакции еще не опубликованы в блокчейне. Для начала нужно сделать еще одну вещь.

Три монеты Боба и три монеты Алисы
Помните, что единственный способ извлечь монеты из кошелька с мультиподписью — это совместная подпись транзакции обеими сторонами, т. е. для отправки всех шести монет Алисы на внешний адрес ей потребуется одобрение Боба. В этом случае ей придется сформировать транзакцию (шесть биткоинов на определенный адрес) и добавить собственную подпись.
Алиса может сразу попытаться транслировать транзакцию, но она будет недействительной, поскольку Боб не поставил свою подпись. Алиса должна предоставить ему незавершенную сделку, и как только он подпишет ее, операция станет действительной.
Однако в данном случае, пока еще не предусмотрен процесс, обязующий участников действовать честно. Как мы уже упоминали ранее, если ваш контрагент отказывается сотрудничать, ваши средства фактически оказываются в ловушке. Давайте перейдем к механизму, который предотвращает это. Для этого есть несколько движущих элементов, которые станут решением такой проблемы.
Чтобы избежать подобной неблагоприятной ситуации, каждая сторона должна придумать секрет, назовем их: As и Bs. Если бы Алиса и Боб раскрыли их, это были бы плохие секреты, поэтому они пока держат их в тайне. Затем пара генерирует хеши соответствующих секретов: h(As) и h(Bs). Таким образом, вместо того, чтобы делиться своими секретами, они обмениваются хешами.

Алиса и Боб обмениваются хешами своих секретов.
Алисе и Бобу необходимо договориться об определенных транзакционных обязательствах перед отправкой переводов на адрес с мультиподписью. Это позволяет обеспечивать безопасность в случае, если кто-то решит присвоить средства.
Если вы думаете о канале, подобном мини-регистру, на который мы ссылались ранее, то транзакционные обязательства — это обновления, которые вы вносите в регистр. Каждый раз, когда вы создаете новую пару транзакционных обязательств, вы делаете ребалансировку средств между двумя участниками.
У Алисы будет два вывода: первый адрес она пополняет, а другой привязывается к новому адресу с мультиподписью. Она подписывает второй адрес и передает его Бобу.

Транзакция Алисы с двумя выводами: один с депозитом на ее собственный адрес, а другой с депозитом на новый адрес с мультиподписью. Однако для последнего все еще нужна подпись Боба, чтобы сделать операцию действительной.
Боб делает то же самое: один адрес его личный, а другой с мультиподписью. Он подписывает его и передает Алисе.
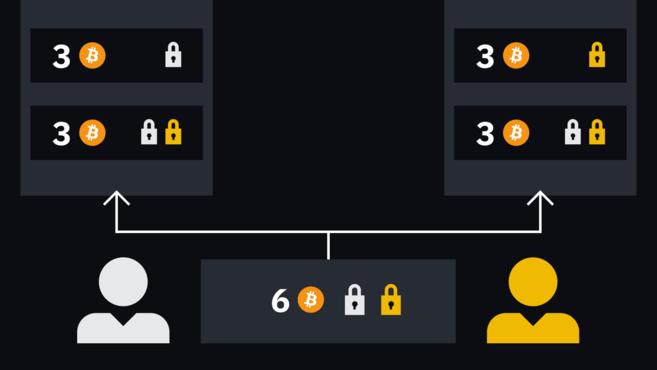
У нас есть две незавершенные транзакции, которые очень похожи.
Алиса может добавить подпись к транзакции Боба, одобрив ее таким образом. Нужно отметить, что эти средства расходуются из мультиподписи по схеме 2 из 2, которая еще не была профинансирована. Это все равно, что пытаться обналичить чек с нулевым балансом. Таким образом, эти частично подписанные транзакции можно будет использовать только после запуска мультиподписи.
Новые адреса с мультиподписью (для которых предназначены 3 выходящих BTC) имеют некоторые специфические свойства. Давайте посмотрим на незавершенную транзакцию, которую Алиса подписала и передала Бобу. Вывод, основанный на мультиподписи, может быть приведен в действие при соблюдении следующих условий:
- Обе стороны выполняют совместную подпись.
- Боб делает перевод самостоятельно по истечении определенного периода времени (в связи с тайм-локом).
- Алиса может потратить баланс, если узнает секрет Боба: Bs.
Для транзакции Боб просит Алису реализовать следующее:
- Обе стороны выполняют совместную подпись.
- Алиса делает перевод самостоятельно по истечении определенного периода времени.
- Боб может потратить баланс, если узнает секрет Алисы: As.
Имейте в виду, что ни одна из сторон не знает секрета другой, поэтому пункт 3 пока не представляется возможным. Следует также отметить, что если вы подпишете транзакцию, ваш контрагент может сразу же потратить деньги, поскольку на их выводе нет особых условий. Вы можете подождать, пока истечет время, чтобы потратить средства самостоятельно, или вы можете скооперироваться с другой стороной, чтобы вывести их в одно время.
Итак, теперь вы можете публиковать транзакции в оригинальном адресе с мультиподписью по схеме 2 из 2. По итогу это безопасно, поскольку вы можете получить свои средства, если ваш контрагент покинет канал.
После подтверждения транзакции канал запускает операции в обработку. Эта первая пара транзакций показывает нам текущее состояние мини-регистра. На данном этапе, выплаты будут распределены в порядке: 3 BTC Бобу и 3 BTC Алисе.
Когда Алиса захочет осуществить новый перевод Бобу, паре нужно будет создать две новые транзакции, чтобы заменить первый набор. Практика остается такой же: сделки подписаны только наполовину. Однако Алиса и Боб должны будут отказаться от своих старых секретов и обменятся новыми хешами для следующего раунда транзакций.

Например, если Алиса хочет заплатить Бобу 1 BTC. Две новые транзакции зачисляют 2 BTC Алисе и 4 BTC Бобу. Таким образом, баланс обновится.
Каждая из сторон может в любое время подписать и передать другому последние транзакции, чтобы осуществить расчет, т.е. зафиксировать финальную информацию в блокчейне. Тот кто сделает это, должен будет подождать истечение тайм-лока, в то время как другая сторона может потратить средства сразу, в момент их получения. Стоит отметить, что если Боб подписывает и транслирует транзакцию Алисе, у нее появляется возможность выхода без каких-либо дополнительных условий.
Обе стороны могут вместе закрыть канал (осуществить кооперативное закрытие) — это самый простой и быстрый способ вернуть средства обратно в сеть. Но даже если одна из сторон перестает отвечать на запросы или отказывается сотрудничать, другая может вернуть свои средства по истечении тайм-лока.
Предотвращение мошенничества в Lightning Network
Возможно, вы уже распознали возможный вектор атаки. Если сейчас баланс Боба составляет 1 BTC, что помешает ему выбрать старую транзакцию, где у него больше монет? Он ведь уже получил подпись от Алисы, и ему нужно лишь добавить свою подпись и отправить транзакцию в блокчейн, так?
От таких действий его удерживает риск потерять весь свой баланс. Допустим, он решает поступить так и отправляет свою старую транзакцию, которая передает Алисе одну монету, а пять отправляет на адрес с мультиподписью, упомянутый ранее.
Алиса получает одну монету незамедлительно. В свою очередь, Боб должен ожидать, пока истечет тайм-лок, чтобы расходовать баланс адреса с мультиподписью. Если вы помните другое условие, которое было упомянуто выше, то вы скорее всего догадались, что позволит Алисе немедленно потратить тот же самый баланс. Ей нужен секрет, которого у нее тогда не было. Она имеет такую возможность с момента, когда был создан второй раунд транзакций, ведь Боб передал ей этот секрет.
Пока Боб находится в ожидании истечения тайм-лока, не в состоянии что-либо сделать, Алиса может переместить эти средства. Этот механизм, основанный на санкции, предполагает, что участник вряд ли захочет попытаться мошенничать, по той простой причине, что в таком случае, другая сторона сразу получает доступ к их общим монетам.
Маршрутизация платежей
Мы ранее затрагивали эту тему: каналы могут контактировать между собой. В противном случае Lightning Network не была бы так полезна для различных платежей. Вы ведь не собираетесь заблокировать 500$ в канале с кафе, чтобы получать ежедневные фиксации в течение следующих нескольких месяцев?
Но вам не нужно так делать. Если Алиса открывает канал с Бобом, а у него есть канал с Кэрол, Боб получает возможность отправлять платежи, используя связь между ними. Данный механизм работает в несколько «прыжков», что означает, что Алиса может быстро перевести средства любому, к кому существует подобный путь.

В этом случае Алиса может воспользоваться несколькими путями для взаимодействия с Фрэнком. Как правило, она будет выбирать наиболее простой.
За свою роль в маршрутизации посредники могут взимать небольшую плату (не является обязательным). Поскольку Lightning Network относительно новая концепция, рынок комиссионных сборов пока еще не сформировался. Многие ожидают увидеть комиссию, основанную на ликвидности провайдеров.
В базовой цепочке ваша комиссия зависит от того, какое место занимает ваша транзакция в блоке. Сумма транзакции не имеет значения: комиссия для переводов от 1$ до 10 000 000$ будут одинаковой. Для сравнения, в Lightning Network отсутствует такое понятия, как место в блоке.
Вместо этого здесь используется концепция локальных и удаленных балансов. Локальный баланс — это сумма, которую можно «подтолкнуть» на другой конец канала, а удаленный баланс — это сумма, которую может подтолкнуть к вам контрагент.
Рассмотрим еще один пример. Давайте изучим один из приведенных путей: Алиса <> Кэрол <> Фрэнк.

Балансы пользователей до и после перевода 0,3 BTC от Алисы к Фрэнку.
Алиса <> Кэрол и Кэрол <> Фрэнк имеют общую пропускную способность в 1 BTC. Локальный баланс Алисы составляет 0,7 BTC. Если бы они решили сейчас осуществить расчет в блокчейне, она получила бы 0,7 BTC, а Кэрол — свой удаленный баланс (то есть 0,3 BTC).
Если Алиса хочет отправить 0,3 BTC Фрэнку, она отправляет 0,3 BTC к Кэрол. Затем Кэрол производит вывод 0,3 BTC со своего локального баланса в канал с Фрэнком. В результате баланс Кэрол остается прежним: +0,3 BTC от Алисы и -0,3 BTC для Фрэнка исключают все сторонние операции.
Кэрол ничего не теряет, выступая в качестве связующего звена с Фрэнком, но она делает себя менее гибкой. Видите ли, теперь она может потратить 0,6 BTC в своем канале с Алисой и только 0,1 BTC в канале с Фрэнком.
Вы можете представить себе ситуацию, когда Алиса подключена только к Кэрол, а Фрэнк к гораздо более широкой сети. Раньше Кэрол могла отправлять в общей сложности 0,4 BTC другим, через Фрэнка, но теперь она может предложить только 0,1 BTC, потому, что все ее средства находятся на другом конце канала.
В этом случае Алиса успешно поглощает ликвидность Кэрол. Кэрол, в свою очередь, не хочет и дальше ослаблять свою позицию, поэтому она ставит условие: направлять каждые 0,01 BTC с комиссией в десять сатоши. Таким образом, чем больше локальных балансов будут осуществлять транзакции на условиях Кэрол, тем прибыльнее будет ее позиция.
Мы упоминали ранее, что фактические требования к комиссии отсутствуют. Одни могут не беспокоиться о снижении ликвидности, в то время как другие будут открывать каналы исключительно для сбора комиссий.
Недостатки Lightning Network
Было бы замечательно, если Lightning Network стала решением всех проблем с масштабируемостью биткоина. К сожалению, у концепции есть свои недостатки, которые могут помешать этому.
Удобство использования
Биткоин — не самая интуитивно понятная система для новичков: адреса, комиссии и все остальное могут сбить с толку при первом знакомстве, но кошельки могут избавить вас от таких сложных вещей и предложить нечто похожее на существующие платежные системы: скачайте кошелек для смартфона, добавьте в него монеты, и можете начинать работу.
Пока что это является невозможным для Lightning Network. Варианты использования на текущий момент очень ограничены, тем более, когда речь заходит о приложениях для смартфонов. Причина в том, что Lightning-нодам требуется доступ к ноде биткоина для полноценной работы.
После установки клиента, пользователям также необходимо начать открывать каналы, прежде чем они получат возможность совершать платежи. Это может занять много времени и скорее всего будет сложно для новичка по причине ознакомления с множеством терминов, включая входящую/исходящую пропускную способность.
Тем не менее, технологии постоянно совершенствуются, уменьшая порог для входа, и становятся более доступными для пользователей.
Ликвидность
Одной из главных проблем Lightning Network является то, что ваши финансовые возможности ограничены. Вы не можете потратить больше, чем заблокировано в канале. Если все средства распределятся на удаленных балансах, скорее всего вам придется закрыть канал. В качестве альтернативы, вы можете подождать, пока вам кто-то заплатит, но это далеко не идеальное решение.
Пути также могут быть ограничены общей пропускной способностью канала. Рассмотрим это на предыдущем примере: Алиса <> Кэрол <> Фрэнк. Если канал Алисы и Кэрол располагает суммой в 5 BTC, а канал Кэрол и Фрэнка — только 1 BTC, Алиса не сможет отправить через них более 1 BTC. Однако даже в этом случае необходимо перенести баланс на сторону Кэрол в канале Кэрол <> Фрэнк. Данный недостаток может серьезно ограничить пропускную способность LN-каналов, что повлияет на удобство использования.
Централизованные хабы
Из-за проблемы, упомянутой в предыдущем разделе, существует некоторая обеспокоенность о том, что сеть будет способствовать развитию крупных «хабов». Это предполагает появление тесно связанных организаций с большой ликвидностью, где любые значительные платежи будут направляться через некоторые из них.
Очевидно, такой вариант развития событий не является благоприятным. Это ослабит систему, так как выход таких провайдеров в автономный режим приведет к существенному нарушению отношений между элементами системы. Существует также повышенный риск цензуры по причине наличия нескольких точек, через которые проходят транзакции.
Текущая стадия развития Lightning Network
По состоянию на апрель 2020 года Lightning Network развивается достаточно успешно. Сеть насчитывает 12 000+ нод в режиме онлайн, 30 000+ активных каналов и чуть более 920 циркулирующих BTC.

Карта расположения актуальных нод в сети Lightning Network. Источник: explorer.acinq.co
Существует несколько различных реализаций для запуска ноды — одними из самых популярных являются c-lightning от Blockstream, Lightning Network Daemon от Lightning Labs и Eclair от ACINQ. Пользователи, которые не хотят вникать в технические аспекты, могут воспользоваться нодами Plug-and-Play. От них потребуется лишь включить устройство и свободно работать в Lightning Network.
Резюме
С момента запуска майннета в 2018 году сеть Lightning Network значительно расширилась, несмотря на популярное мнение о том, что она все еще находится на стадии бета-версии.
На данном этапе развития, есть некоторые ограничения в удобстве использования, к примеру: для работы Lightning-ноды от вас потребуется некоторая техническая компетентность, но по мере развития ожидается уменьшение порога для входа.
Если все упомянутые проблемы смогут быть решены, Lightning Network может стать неотъемлемой частью экосистемы биткоина, что значительно повысит масштабируемость и скорость транзакций.