Введение
Появляние биткоина положило начало новой концепции – не требующей доверия системы с цифровым дефицитом. До его появления скопировать что-либо в цифровом виде было очень легко, но благодаря технологии блокчейн теперь можно создавать дефицит продуктов в цифровой среде, приближая виртуальный мир к реальному.
Именно эта идея лежит в основе работы невзаимозаменяемых токенов (NFT) или криптоколлекционных предметов. В отличие от криптовалют, где все токены равны друг другу и взаимозаменяемы, NFT уникальны и ограничены в количестве.
NFT – один из основополагающих элементов новой цифровой экономики на основе блокчейна. Их можно использовать в различных областях: играх, цифровой идентификации, лицензировании, сертификатах и искусстве. Более того, NFT даже позволяют разделить владение ценными предметами между несколькими пользователями.
Процесс выпуска NFT стал намного проще, и с каждым днем их создается все больше и больше. В этой статье вы узнаете о принципах работы NFT, их применении и о том, как игра CryptoKitties в конце 2017 года изменила блокчейн Ethereum.
Что такое невзаимозаменяемые токены (NFT)?
Невзаимозаменяемый токен (NFT) – это разновидность криптографического токена в блокчейне, которая представляет собой уникальный актив. NFT могут быть как полностью цифровыми активами, так и токенизированными версиями физических активов. NFT уникальны и не заменяемы, поэтому зачастую эти токены используются в качестве доказательства подлинности предмета и права собственности в цифровой среде.
Взаимозаменяемость означает, что отдельные единицы актива практически неотличимы и могут заменять друг друга. Например, фиатные валюты взаимозаменяемы, потому что каждая единица ничем не отличается от другой эквивалентной единицы: банкноту в 10 долларов можно легко заменить любой другой банкнотой в 10 долларов. Это необходимое качество для актива, который служит средством обмена.
Взаимозаменяемость является одним из основных свойств валюты, позволяющим свободно обмениваться подобными денежными единицами, причем их историю невозможно отследить. Однако данное свойство никак не распространяется на предметы коллекционирования.
А что, если бы мы могли создавать цифровые активы наподобие биткоина, добавляя уникальный идентификатор к каждой единице? Тогда каждая из них стала бы отличной от всех других (т. е. невзаимозаменяемой) – в этом и есть суть NFT.

Как работает NFT?
Существуют различные правила создания и выпуска NFT. Самым известным из них является ERC-721 – стандарт выпуска и торговли невзаимозаменяемыми активами в блокчейне Ethereum.
Более современным улучшенным стандартом является ERC-1155. Он расширяет возможности цифровых активов, позволяя вносить в один контракт как взаимозаменяемые, так и невзаимозаменяемые токены. Стандартизация эмиссии NFT обеспечивает более высокую степень совместимости – уникальные активы можно относительно легко и удобно переводить между различными приложениями.
Сеть Binance Smart Chain (BSC) имеет собственные стандарты NFT: BEP-721 и BEP-1155. Они предоставляют те же возможности, что и ранее упомянутые стандарты Ethereum, однако пользуются бóльшей популярностью среди пользователей, так как их стоимость значительно ниже.
Для коллекционирования и хранения NFT можно использовать Trust Wallet. Как и другие токены блокчейна, ваши NFT будут находиться на адресе пользователя. Стоит отметить, что NFT не могут быть воспроизведены или переведены без разрешения владельца – даже их создателем.
NFT можно продавать на открытых торговых площадках, в том числе Treasureland, BakerySwap, Juggerworld на BSC и OpenSea на Ethereum. Эти рынки предоставляют продавцам каналы связи с покупателями для торговли уникальными токенами, стоимость которых изменяется в соответствии с рыночным спросом.
В чем заключается ценность NFT? Ценность NFT, как и других ценных вещей, определяется не столько их качествами, сколько людьми, для которых они что-то значат. Иными словами, стоимость таких активов определяется верой в их ценность. Будь то фиатные деньги, драгоценные металлы или транспортное средство – эти вещи имеют ценность, потому что так считают люди. И если предметы становятся ценными просто в силу чьих-то убеждений, то почему нельзя поверить в ценность цифрового предмета?
Для чего используется NFT?
NFT можно использовать в децентрализованных приложениях (DApps) для выпуска уникальных цифровых активов и применять их для коллекционирования, инвестиций и многого другого.
В игровой экономике нет ничего нового – многие онлайн-игры давно уже имеют свою собственную устоявшуюся экономическую модель. В этом смысле использование блокчейн-технологии для токенизации игровых активов является всего лишь еще одним шагом вперед. По сути дела, использование NFT может потенциально решить или смягчить общую проблему инфляции, характерную для многих игр.
По мере развития цифрового пространства появился еще один интересный способ использования NFT: токенизация активов реального мира. Такие NFT представляют собой доли физических активов, которые могут храниться и продаваться как токены в блокчейне. Это дарит многим рынкам необходимую ликвидность, так как без использования NFT они бы не смогли торговать теми же коллекционными предметами, недвижимостью, предметами искусства и многим другим.
Еще одной сферой применения NFT является цифровая идентификация. Хранение идентификационной информации и данных о владении чем-либо в блокчейне повышает целостность информации и конфиденциальность пользователей по всему миру. В то же время простая и не требующая доверия система перевода этих активов может избавить нас от множества актуальных проблем в мировой экономике.
Как создать NFT?
Создать собственные NFT на основе BSC или Ethereum очень просто, и сделать это можно на многочисленных платформах и биржах NFT. Для этого вам понадобится немного криптовалюты для оплаты комиссии за создание и цифровой файл, который вы превратите в NFT. Кроме того, вам необходимо выбрать платформу для создания NFT: Ethereum или Binance Smart Chain.
Традиционным местом появления и развития NFT является Ethereum. У этой платформы большая база пользователей и развитое NFT-сообщество, однако из-за высокой комиссии небольшие покупки, продажи и транзакции получаются очень дорогими. BSC – это более новый блокчейн, но на его рынках NFT уже наблюдается значительный рост, а транзакции намного дешевле.
Как купить NFT?
Как мы уже говорили, выбор торговой площадки NFT – первое, на что следует обратить внимание при покупке невзаимозаменяемых токенов. Но так же важно разобраться и со способом оплаты. NFT нельзя купить с помощью кредитной карты или PayPal – вам понадобится криптокошелек и некоторое количество криптовалюты.
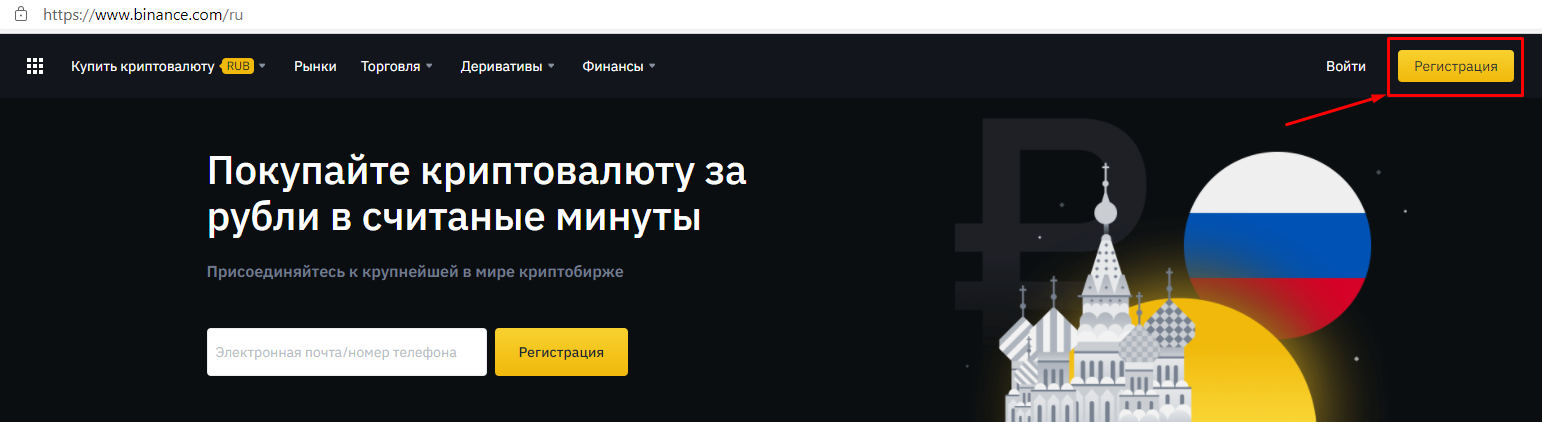
Для NFT в Binance Smart Chain цены почти всегда будут в BNB, тогда как в Ethereum в качестве валюты обычно используется эфир (ETH). Обе эти криптовалюты доступны для покупки на бирже Binance. После приобретения выбранной криптовалюты переведите средства в кошелек для работы с NFT-маркетплейсами.
Для этого вам подойдут кошельки-расширения для браузера Binance Chain Wallet и MetaMask с возможностью подключения к торговой площадке NFT. Вам просто нужно перевести свою криптовалюту с Binance в кошелек, перейти на сайт торговой площадки и подключить свой кошелек (кнопка подключения обычно находится в правом верхнем углу). Остерегайтесь поддельных или подозрительных сайтов: перепроверьте URL-адрес и сохраните выбранный сайт в закладках, если планируете часто его использовать.
Если вы предпочитаете пользоваться кошельком на смартфоне, попробуйте Trust Wallet. Сервис доступен на iOS и Android и поддерживает несколько блокчейнов. Не забывайте, что за транзакции с Ethereum и BSC также взимается плата! Потому всегда старайтесь иметь дополнительную криптовалюту для оплаты комиссий.
История криптокотиков и эфириума
Одним из первых популярных проектов с NFT была игра CryptoKitties, созданная на базе Ethereum. В ней игроки собирают, разводят и обмениваются виртуальными кошками.

Каждая кошка CryptoKitty имеет определенные характеристики, такие как возраст, порода или цвет – то есть каждая из них уникальна и невзаимозаменяема. Кроме того, токен CryptoKitty невозможно разделить на более мелкие части (как эфир на гвеи).
Игра CryptoKitties известна тем, что перегрузила блокчейн Ethereum из-за большого количества пользователей. Около 25% трафика Ethereum в декабре 2017 года приходилось на этих коллекционных кошек. Игра оказала большое влияние на развитие Ethereum, но этому способствовали и другие факторы, в том числе бум первичного предложения монет (ICO).
CryptoKitties – один из первых примеров использования блокчейна не для создания валюты, а для развлечения и отдыха. Суммарно эти виртуальные кошки привлекли миллионы долларов, а особо редкие из них были проданы за сотни тысяч долларов каждая.
Популярные проекты, использующие NFT и криптоколлекционирование
Многие проекты уже используют NFT в качестве коллекционных и торгуемых предметов. Давайте рассмотрим самые популярные:
Decentraland
Decentraland – это децентрализованный виртуальный мир, в котором игроки могут владеть и обмениваться частями виртуальной земли и другими игровыми элементами NFT. Cryptovoxels – похожая игра, в которой можно строить, развивать и обмениваться виртуальной собственностью.

Alchemy Toys
Alchemy Toys – это игра BSC, в которой NFT выступают в качестве игрушек с уникальными серийными номерами. Игроки собирают эти игрушки как NFT, комбинируют их для создания игрушек более высокого уровня или приносят в жертву богам (сжигают). В игре присутствует и финансовый аспект с покупкой и продажей этих игрушек.
Чтобы выиграть, необходимо собрать все 127 игрушек и пожертвовать их для «достижения просветления». Первый игрок, достигший просветления в каждом раунде (эпохе), получает долю сокровищ храма (в BNB).
PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap – самый востребованный автоматизированный маркет-мейкер в сети BSC с точки зрения объема. Именно PancakeSwap выпускает наиболее популярные NFT – коллекционных кроликов, которых часто разыгрывают среди пользователей платформы. Некоторые из них являются сугубо декоративными, а другие можно обменять на CAKE – собственный токен платформы.
Gods Unchained
Gods Unchained – это цифровая коллекционная карточная игра, в которой карты выпускаются в виде NFT на блокчейне. Поскольку каждая цифровая карта уникальна, игроки могут собирать их и продавать так же, как и физические.

Cryptopunks
Cryptopunks – это коллекционные картинки, каждая из которых изображает уникального 8-битного NFT-персонажа. Данный проект стал толчком к созданию стандарта токенов ERC-721 и был одним из первых примеров увлечения людей криптоискусством. С тех пор персонажи CryptoPunks продавались за миллионы долларов и вдохновили множество похожих проектов по всему миру.
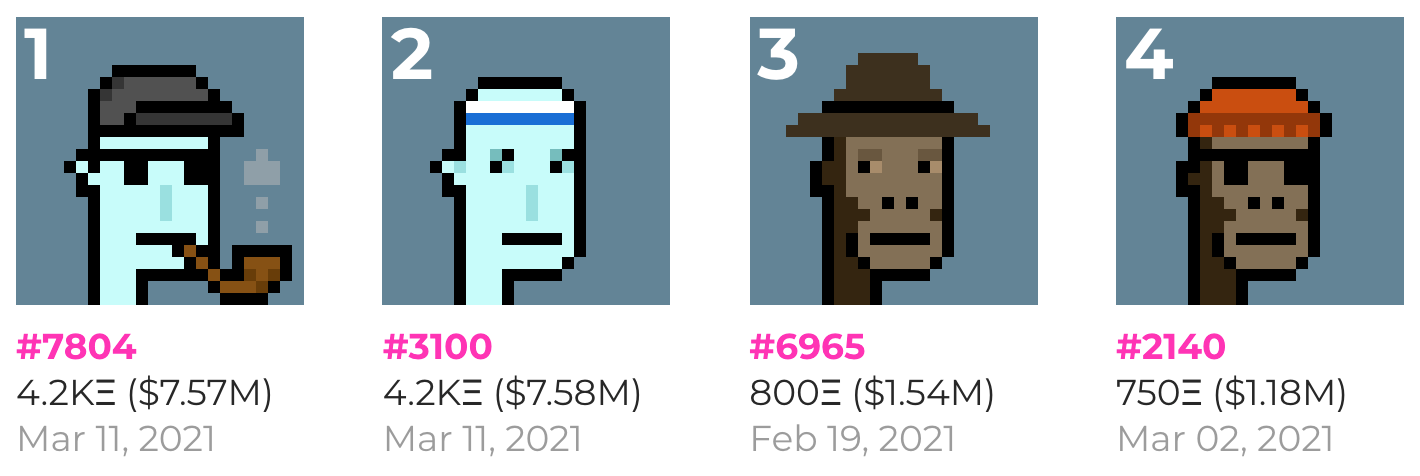
My Crypto Heroes
My Crypto Heroes – многопользовательская ролевая игра (RPG), в которой игроки повышают уровни исторических героев с помощью квестов и сражений, а герои и игровые предметы выдаются в виде токенов в блокчейне Ethereum.

Binance Collectibles и NFT
Периодически Binance разыгрывает NFT и поощряет токенами особо активных пользователей. Вы можете регулярно получать коллекционные предметы Binance с возможностью продажи – от торговых фьючерсов до токенов Pizza Day.
Платформа также раздает Binance Collectibles – NFT, выпущенные в сотрудничестве с Enjin. Если вы хотите получить такой токен, обязательно подпишитесь на Binance в Twitter и ждите следующих розыгрышей! Для участия в розыгрыше NFT выполните следующие действия:
-
Скачайте кошелек с поддержкой Ethereum, например Trust Wallet.
-
Скопируйте свой адрес Ethereum и предоставьте его в соответствии с условиями конкурса: отправьте с помощью специальной формы или оставьте в комментариях к посту в Twitter. Ознакомьтесь с правилами, чтобы точно знать условия участия.
-
Если вы выиграли NFT и вам его перевели, он отобразится во вкладке «Коллекционирование» в Trust Wallet. С этого момента вы можете либо удерживать его, либо продавать на P2P-маркетплейсах.
В ближайшее время Binance запустит NFT-маркетплейс, который даст пользователям возможность создавать и торговать NFT. В нем будут представлены эксклюзивные NFT от известных авторов по всему миру, включая музыканта Льюиса Капальди и криптохудожника Тревора Джонса. Платформа также предложит авторам роялти за последующие продажи через маркетплейс.
Crypto Stamps
Австрийская почтовая служба начала производить криптовалютные марки, соединив тем самым цифровой мир с реальным. Как и любые другие марки, они используются для перевозки почтовых грузов, но также сохраняются в виде цифровых изображений в блокчейне Ethereum, что в последующем делает их привлекательными предметами коллекционирования.

Резюме
Цифровые предметы коллекционирования открыли для технологии блокчейн совершенно новые возможности за пределами традиционных финансовых приложений. Представляя физические активы в цифровом формате, NFT становятся важной частью экосистемы блокчейн и экономики в целом.
Вариантов использования таких токенов множество, и вполне вероятно, что скоро многие разработчики предложат новые захватывающие идеи применения этой многообещающей технологии.