Что такое криптовалюта?
Криптовалюта – это цифровая форма денежных средств, которая позволяет людям передавать ценности или обмениваться ими в цифровой среде.
Возможно, вы спросите, чем такая система отличается от PayPal или банковского приложения, установленного на вашем телефоне. На первый взгляд все они, безусловно, служат для одной и той же цели: обмениваться деньгами с друзьями, совершать покупки на любимом веб-сайте и т.д. Но под внешней оболочкой этих систем кроется совершенно разный принцип работы.
Что делает криптовалюту уникальной?
Криптовалюта уникальна по многим причинам. Основная ее функция заключается в том, чтобы выступать в качестве системы электронных денежных средств, способной работать без участия какого бы то ни было контролирующего органа или центрального банка.
Хорошая криптовалюта должна быть децентрализована. В такой системе не будет ни центрального банка, ни определенной группы людей, влияющей на принятие решений. Участники сети (ноды) через свое программное обеспечение связываются друг с другом и обмениваются информацией между собой.
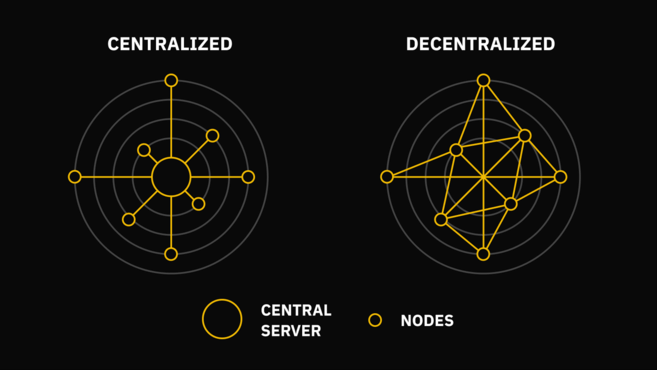 Централизованные и децентрализованные сети.
Централизованные и децентрализованные сети.
На изображении слева продемонстрировано взаимодействие участников в стандартной банковской системе. Вы можете заметить, что вся работа данного механизма построена на необходимости контакта с центральным севером. В представленной же на изображении справа децентрализованной структуре отсутствует подобная иерархия, поскольку функционирование сети основано на работе взаимосвязанных нод, которые постоянно обмениваются информацией между собой.
Децентрализация сетей криптовалют защищает их от отключения или цензуры. Чтобы отключить централизованную сеть, достаточно просто вывести из строя главный сервер. Например, если банк уничтожит свою базу данных и все резервные копии, восстановить данные о балансах пользователей будет очень тяжело. Криптовалютные ноды хранят копию базы данных и каждая функционирует как отдельный сервер. Некоторые из нод могут выходить в автономный режим, но другие участники по-прежнему будут обмениваться информацией через них.
Кроме того, криптовалюты работают 24 часа в сутки круглый год. Они позволяют переводить средства в любую точку мира без привлечения посредников. Именно поэтому их часто называют общедоступными: для перевода средств достаточно иметь выход в интернет.
Почему такой тип активов называют криптовалютами?
Термин «криптовалюта» образован сочетанием слов криптография и валюта. Для защиты транзакций криптовалюты широко используют криптографические методы. Отсюда и название.
Что такое криптография с открытым ключом?
В основе криптовалютных сетей лежит система криптографии с открытым ключом. Именно она обеспечивает безопасность пользователей во время совершения транзакций.
В этой системе у пользователя есть публичный ключ и приватный ключ. Приватный ключ – это огромное число, которое невозможно угадать. Зачастую даже трудно осознать, насколько оно большое.
В случае с биткоином угадать приватный ключ – все равно, что правильно угадать результат подбрасывания монеты 256 раз подряд. Скорее Земля перестанет вращаться, чем современные компьютеры успеют взломать такой ключ.
В любом случае, как следует из названия, приватный ключ нужно держать в секрете. С его помощью вы сгенерируете публичный ключ, который можно смело предоставлять кому угодно, поскольку на его основе практически невозможно восстановить информацию о вашем приватном ключе.
С помощью приватного ключа вы также можете создавать цифровые подписи. Это похоже на подписание документов в реальной жизни.Главное отличие состоит в том, что действительность подписи легко определяется путем ее сравнения с соответствующим публичным ключом. Таким образом, пользователю не нужно раскрывать свой приватный ключ, но он может доказать факт владения им.
Если вы захотите потратить свои средства в криптовалюте, вы сможете это сделать только при наличии соответствующего приватного ключа. При совершении транзакции вы объявляете всем в сети, что собираетесь перевести средства. Информация об операции содержится в сообщении (транзакции), которое подписывается и добавляется в базу данных криптовалюты (блокчейн). Как уже говорилось, для создания цифровой подписи необходим ваш приватный ключ. А поскольку база данных видна всем пользователям, любой может проверить действительность вашей транзакции по этой подписи.
Кто создал криптовалюту?
На протяжении многих лет предпринимались различные попытки создания систем цифровых валют, но первая криптовалюта появилась лишь в 2009 году, и это был биткоин. Его разработал человек или группа людей под псевдонимом Сатоши Накамото, однако настоящая личность создателя по сей день остается неизвестной.
Биткоин стал прародителем огромного числа криптовалют. Одни нацелены превзойти его, у других уже есть свои особенности и преимущества, которые нет у биткоина. Сегодня многие блокчейны позволяют пользователям не только обмениваться денежными средствами, но и запускать децентрализованные приложения, используя смарт-контракты. Ethereum – пожалуй, самый яркий пример такого блокчейна.
В чем разница между криптовалютами и токенами?
На первый взгляд кажется, что криптовалюты и токены – это одно и то же. Оба вида активов используются для торговли на биржах и могут передаваться между адресами блокчейна.
Криптовалюты используются исключительно в качестве денег, будь то средство обмена, сбережения или и то и другое. Каждая единица функционально взаимозаменяема, то есть одна монета равна по стоимости другой.
Биткоин и другие первые криптовалюты были разработаны исключительно как цифровые деньги, но появившиеся позднее блокчейны стремятся к большему. Например, Ethereum не только выполняет функцию валюты, но также позволяет разработчикам запускать код (смарт-контракты) в распределенной сети и создавать токены для различных децентрализованных приложений.
Токены, в свою очередь, можно использовать как криптовалюты, но они гораздо более гибкие. Вы можете создать миллионы одинаковых токенов или несколько особенных, обладающих уникальными свойствами. Они могут быть чем угодно – от цифровых чеков, представляющих собой долю в компании, до баллов лояльности.
В протоколе с поддержкой смарт-контрактов базовая валюта (используемая для оплаты транзакций или приложений) отделена от токенов. Например, в Ethereum собственной валютой является эфир (ETH), и она используется для создания и передачи токенов внутри сети Ethereum. Создаются они в соответствии со стандартами вроде ERC-20 или ERC-721.
Что такое криптовалютный кошелек?
В криптокошельке хранятся ваши приватные ключи. Он может быть отдельным устройством (аппаратный кошелек), приложением на вашем ПК/смартфоне или даже листом бумаги.
Кошельки позволяют пользователям взаимодействовать с криптовалютной сетью и осуществлять транзакции. Разные типы кошельков имеют разную функциональность. Бумажный кошелек, например, не даст вам возможности подписывать транзакции или отображать текущие цены в фиатной валюте.
Наиболее удобными для повседневных платежей считаются программные кошельки (например, Trust Wallet), но с точки зрения безопасности предпочтение отдается аппаратным кошелькам. Держатели криптовалют, как правило, пользуются обоими типами кошельков.
Как работает блокчейн?
Что такое блокчейн?
Блокчейн – это особый вид базы данных, в которую данные можно только вносить, а не удалять или изменять. Транзакции внутри так называемых блоков (состоящих из информации о транзакциях и других метаданных) периодически добавляются в блокчейн.
Такая структура называется цепочкой, потому что метаданные каждого блока включают в себя часть информации из предыдущего и связывают блоки между собой. В частности, туда входит хеш предыдущего блока, который работает как уникальный цифровой отпечаток.
Вероятность того, что два фрагмента данных дадут вам одинаковый результат хеш-функции, невероятно мала. То есть, если кто-то попытается изменить старый блок, его хеш также изменится, а значит, и хеш следующего блока тоже будет другим, и так далее. Следовательно, понять, был ли изменен блок, очень просто, ведь изменены будут и все следующие за ним блоки.
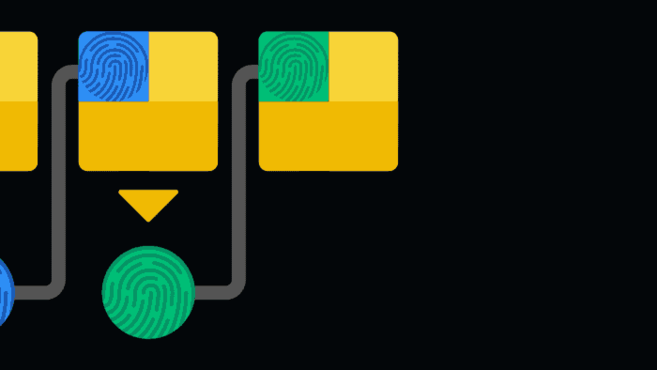 Хеш каждого блока используется в следующем блоке. Это формирует так называемую цепочку из блоков или блокчейн.
Хеш каждого блока используется в следующем блоке. Это формирует так называемую цепочку из блоков или блокчейн.
Важно отметить необходимость полной загрузки блокчейна на накопитель участника. Помните, мы говорили о том, что любой желающий может осуществлять валидацию (проверку) транзакций и подписей с помощью криптографии с открытым ключом? Когда нода получает блок, она выполняет ряд проверок; если что-то является недопустимым, блок отклоняется.
Когда нода получает валидный блок, она копирует его и распространяет этот блок на другие ноды. Они, в свою очередь, делают то же самое, пока блок не распространится по всей сети. Такой же процесс выполняется и для неподтвержденных транзакций, то есть тех, которые были объявлены, но еще не добавились в блокчейн.
Как блоки добавляются в блокчейн?
Поскольку система держится на взаимосвязанных между собой блоках, целостность всей блокчейн-сети подрывается в случае записи хотя бы одной ложной информации. В то же время в такой распределенной системе отсутствует администратор или руководитель, который бы поддерживал работу системного регистра или главной бухгалтерской книги системы. В связи с этим возникает вопрос: что выступает в качестве гаранта честной работы всех участники сети?
Сатоши предложил систему Proof of Work (Доказательство выполнения работы), которая дала возможность любому пользователю выдвигать блок на добавление в блокчейн. Чтобы выдвинуть блок, пользователи должны предоставить вычислительные мощности для решения задач, установленных протоколом.
Proof of Work – это проверенная схема достижения консенсуса среди пользователей, но далеко не единственная. Альтернативы, такие как Proof of Stake, продолжают тестироваться, однако они пока не достигли уровня реализации в их истинной форме (несмотря на то, что гибридные механизмы консенсуса существуют уже довольно долго).
Как работает майнинг криптовалюты?
Выше изображен процесс под названием майнинг. Если майнер найдет решение задачи, построенный им блок расширит цепочку. В результате он получит вознаграждение в родной валюте блокчейна.
Задачи, которые майнеры должны решать, требуют постоянного хеширования данных для получения числа ниже определенного значения. Хеширование с помощью односторонней функции означает, что, имея выходные данные, угадать входные данные практически невозможно. И наоборот: при наличии входных данных проверить выходные данные уже очень легко. Таким образом, любой пользователь может проверить, что майнер создал «правильный» блок и отклонить невалидные блоки. В последнем случае майнер не получит вознаграждения и впустую потратит свои ресурсы.
В результате вырисовывается такая концепция игры, при которой попытка обмана обходится очень дорого, а честность поощряется. Ни у одного злоумышленника не хватит ресурсов, чтобы бесконечно атаковать сильную сеть. Таким образом, пользователи с ресурсами могут получать доход путем честного участия в процессе.
Могут ли криптовалюты масштабироваться?
Вероятно, вы скажете, что распределенные сети не очень продуктивны. К сожалению, криптовалюты могут быть безопасными и устойчивыми к цензуре лишь в том случае, если все ноды регулярно синхронизируют копию блокчейн-сети. И чем ниже требования к синхронной активности участников, тем проще процесс присоединения новых участников.
Таким образом, блокчейн, ориентированный на добавление маленьких блоков каждые десять минут, предпочтительнее, чем тот, который добавляет один огромный блок каждые пять минут. Вариант с большим блоком предполагает ноды с наличием высокопроизводительных компьютеров, чтобы поддерживать регулярную синхронизацию и подталкивать маломощные устройства к отключению. Подобный подход в итоге приводит к большей централизации, поскольку конкуренция в сети становится всё меньше.
Но с маленькими блоками мы не можем достичь большого количества транзакций в секунду (TPS). Кроме того, в загруженные периоды добавление блоков в блокчейн займет больше времени. Это неудобно, если вы хотите произвести быструю оплату, но ради децентрализации приходится идти на компромиссы.
Мы называем эту проблему дилеммой масштабируемости. Хорошо масштабируемая система может легко адаптироваться к повышенной нагрузке. Блокчейны же масштабируются плохо. Как мы уже объясняли, увеличение пропускной способности за счет блоков большего размера подрывает всю цель распределенной сети.
Чтобы увеличить TPS без ущерба децентрализации, применяется подход офчейн-масштабирования. Он включает широкий спектр решений (централизованных и децентрализованных), которые позволяют совершать транзакции без регистрации в блокчейне.
Кто принимает решения по программному обеспечению криптовалюты?
Криптовалютные сети работают в формате добровольного согласия (opt-in). Никто не заставит вас запускать программное обеспечение против вашей воли. Хороший протокол отличается полностью открытым исходным кодом, который пользователи могут проверить и убедиться в честности и безопасности системы.
Как правило, криптовалюты позволяют любому желающему принять участие в их разработке. Новые функции или изменения в коде проверяются сообществом разработчиков до согласования и дальнейшей публикации. Оттуда пользователи могут сами просмотреть код и решить, запускать его или нет.
Некоторые обновления будут иметь обратную совместимость, что даст возможность обновленным нодам взаимодействовать со старыми. В случае с обновлениями без обратной совместимости старые ноды будут отключены от сети, если не обновятся. Чтобы узнать больше, ознакомьтесь с информацией о хардфорках и софтфорках.
Как инвестировать в криптовалюту?
Какую криптовалюту мне стоит купить?
Выбор зависит только от вас. Исследуйте вопрос самостоятельно и примите решение, основываясь на собственном анализе. Также существует множество инструментов, которые могут помочь вам принять правильное решение. Например, Binance Research предоставляет ценные сведения и аналитические материалы о рынке, а также комплексные отчеты по отдельным проектам.
Чтобы лучше понять, какая криптовалюта вам нужна, вам необходимо разобраться в специфике работы каждой из них, а в первую очередь – биткоина. Именно для этого мы подготовили статью «Что такое биткоин?».
Что мне нужно знать, прежде чем инвестировать в криптовалюты?
С чего же начать? Существует множество видов анализа финансовых рынков и множество стратегий, которые используют профессиональные инвесторы. Но в целом эксперты выделяют два основных подхода к оценке инвестиций: фундаментальный анализ (FA) и технический анализ (TA).
Фундаментальный анализ – это метод оценки стоимости актива, основанный на экономических и финансовых факторах. Аналитики, которые используют этот метод, рассматривают как макро-, так и микроэкономические факторы, а также отраслевые условия или бизнес, лежащий в основе актива (если таковой имеется). В случае с криптовалютой просматриваются общедоступные данные блокчейна, которые иногда называют ончейн-метриками.
Сюда относят просмотр количества транзакций, адресов, основных держателей, хешрейта сети и другую разнообразную информацию. Цель анализа – дать оценку актива и сравнить с его текущей оценкой. Этот подход позволяет выяснить, недооценен или переоценен актив в данный момент.
Важно понимать, что криптовалюты – это новый и ещё развивающийся класс активов. А значит, для полноценного, всеобъемлющего фундаментального анализа информации пока недостаточно. Иными словами, на данный момент отсутствует стандартизированный механизм для определения стоимости криптовалюты, и большинству существующих методов нельзя полностью доверять. Успех или провал криптовалютного проекта зависит от множества различных факторов, которые не позволит точно предсказать ни один из имеющихся методов анализа.
Технический анализ опирается на другой подход. В отличие от фундаментального, технический анализ не стремится определить действительную стоимость актива. Вместо этого он оценивает возможности для торговли и инвестиций на основе исторических данных торгов, учитывая движения цен, графические модели, индикаторы и другие инструменты, позволяющие составить представление о силе или слабости рынка. Согласно техническому анализу, предыдущие движения цены актива могут быть полезны для прогнозирования ее будущих изменений.
Поскольку технический анализ может применяться практически на любом рынке при наличии истории торговых операций, он активно используется криптотрейдерами.
Итак, какой анализ предпочесть? Мы рекомендуем оба. Большинство инструментов анализа рынка показывают наибольшую эффективность в сочетании с другими инструментами. В любом случае необходимо понимать финансовые риски, уметь управлять рисками и никогда не инвестировать больше, чем вы готовы потерять.
Где купить криптовалюту
Покупать криптовалюту можно разными способами. Первое, что вам нужно сделать, это конвертировать вашу фиатную валюту в криптовалюту. После этого вы можете удерживать криптовалюту (или «ходлить» (от англ. HODL), торговать ею, обменивать на другие криптовалюты или предоставлять с ней займы и зарабатывать проценты. Давайте подробнее рассмотрим типы криптовалютных бирж.
Централизованные биржи (CEX)
Концепция централизованной биржи может смутить вас своим названием, поскольку криптовалюты чаще всего описываются как децентрализованные. В двух словах, централизованные биржи являются онлайн-платформами, которые облегчают торговлю, соединяя покупателей и продавцов.
Работает это следующим образом. Пользователи вносят свои фиатные деньги или криптовалюту на биржу и торгуют, используя ее внутренние системы. Если вы знакомы с принципом работы криптовалютных кошельков, то вам будет понятно, что в данном случае криптовалюта хранится в кастодиальном кошельке биржи. Но при желании вы легко сможете вывести средства и хранить их в собственном кошельке.
Некоторые пользователи предпочитают хранить средства на бирже, поскольку они регулярно торгуют криптовалютой – или просто для большего удобства. Однако если платформа окажется взломана, средства пользователей могут оказаться под угрозой.
Децентрализованные биржи (DEX)
Децентрализованные биржи (DEX) устроены иначе. Работа на DEX не предполагает никаких посредников. На самом деле, более точное название такого типа биржи – некастодиальная биржа.
Торговля на DEX осуществляется следующим образом. Вместо того чтобы вносить средства на кошелек биржи, вы торгуете напрямую из собственного кошелька. При совершении сделки средства переводятся напрямую в блокчейн посредством смарт-контрактов.
Поскольку на DEX нет посредника, который бы хранил ваши средства, некоторые пользователи считают этот вариант более безопасным, чем CEX. Еще одно преимущество такого рода платформ заключается в том, что большинство децентрализованных бирж не требуют от вас предоставления какой-либо личной информации, кроме адреса кошелька. С другой стороны, хранение средств требует от вас определённых знаний и навыков – ведь только вы несете ответственность за свои сбережения.
P2P-биржи
Одноранговая биржа (P2P) существенно отличается от CEX и DEX. В данном случае сам обменник не участвует в процессе сделки, а является лишь связующим компонентом между покупателем и продавцом. Они в свою очередь могут осуществлять сделку любым способом на свое усмотрение. Таким образом, способ оплаты и депозит определяются покупателями и продавцами самостоятельно для каждой отдельной операции.
Как купить криптовалюту
Как покупать криптовалюты на Binance
- Войдите на Binance или зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет своего аккаунта.
- Перейдите в раздел покупки и продажи криптовалюты.
- Выберите криптовалюту, которую вы хотите купить, и валюту, в которой будете совершать оплату.
- Выберите способ оплаты.
- При необходимости введите данные своей карты или банковские реквизиты, а также подтвердите свою личность.
- На этом всё! Ваша криптовалюта вскоре будет зачислена на ваш Binance-аккаунт.
Как покупать криптовалюты на Binance DEX
Покупка криптовалюты на децентрализованных биржах происходит немного сложнее, чем на других платформах.
Что вам перед этим потребуется:
- кошелек с подключением к Binance DEX (мы рекомендуем Trust Wallet);
- токены Binance (BNB) для оплаты комиссий за транзакции.
Как покупать криптовалюты на Binance P2P
- Войдите на Binance или зарегистрируйтесь, если у вас еще нет своего аккаунта.
- Перейдите в раздел Binance P2P.
- Сделайте выбор: купить или продать криптовалюту.
- Заполните поля в фильтре: валюта, метод оплаты или другие требования к сделке.
- Выберите подходящий вариант, который соответствует всем вашим требованиям, или разместите свой собственный заказ.
Часто задаваемые вопросы о криптовалюте
Является ли криптовалюта легитимной?
Лишь некоторые страны ввели прямой запрет на покупку, продажу и хранение криптовалюты. В подавляющем большинстве государств мира биткоин и другие виртуальные валюты абсолютно легальны. И всё же, прежде чем начать работу с ними, вам следует проверить, одобряет ли это юрисдикция именно вашего государства.
Важно помнить, что в каждой стране свой подход к регулированию криптовалюты. Удостоверьтесь в том, что вы не нарушаете никаких правил, касающихся налогообложения и т.д.
Криптовалюта мертва?

За последние десять лет СМИ сотни раз пророчили смерть криптовалютам. Однако с 2009 года они так никуда и не исчезли. Мы не хотим сказать, что они не волатильны. Напротив, цены на криптовалюты подвержены серьезным колебаниям. Поэтому для тех, кто надеется только получать прибыль, медвежьи рынки могут стать разочарованием.
При этом было бы неправильно называть криптовалюту «мертвой». Она продолжает привлекать всё новых и новых пользователей, а ее технологии и инфраструктура становятся все более замысловатыми.
Инновации, которые несут биткоин и эфириум, несомненно, сыграют важную роль в изменении современных денежных систем, чтобы они лучше вписывались в современную эпоху. Неизменяемость, устойчивость к цензуре, надежность и почти мгновенные транзакции с использованием общественной денежной системы могут полностью изменить принципы экономической деятельности в интернете.
Является ли криптовалюта безопасной?
Криптовалюта предполагает некоторую степень риска. К примеру, если вы забыли пароль для доступа к своему банковскому счету, то вы можете просто сбросить его через службу поддержки, но если вы забудете или потеряете приватный ключ, который даёт доступ к вашим активам, никто не сможет вам помочь. Использование надежной биржи может быть более щадящим вариантом. Да, она требует доверия, но вы не рискуете потерять свои приватные ключи.
Криптографическую систему с открытым ключом еще никому не удавалось взломать. Вас, скорее, взломают на любом другом онлайн-ресурсе с самыми надежными методами защиты, чем похитят ваши средства в криптовалюте. Для обеспечения защиты важно быть осведомленным о распространенных способах мошенничества (таких как социальная инженерия, фишинг и т. д.), всегда хранить ваши приватные ключи офлайн и держать их резервные копии в безопасном месте.
Является ли криптовалюта анонимной?
Ваше имя не привязывается к криптовалютным адресам – они всегда выглядят как случайные последовательности цифр и букв в блокчейне. Однако не стоит думать, что при этом достигается полная анонимность. Для идентификации в сети используется ваш псевдоним. Это то же самое имя, просто не такое, как в реальной жизни.
Есть определенные методы, с помощью которых можно связать IP-адреса с вашими действиями. Так, например, пылевые атаки и другие методы анализа могут быть использованы для того, чтобы вас идентифицировать. Помните: блокчейны по своей сути – это огромные общедоступные базы данных. Если вы беспокоитесь о своей конфиденциальности, постарайтесь сделать так, чтобы другим пользователям было тяжело связать ваши операции с вашим именем. Криптовалюты типа биткоина по умолчанию не являются конфиденциальными, но такие методы, как смешивание монет или CoinJoins, могут сделать эвристический анализ ненадежным.
Небольшая подгруппа криптовалют (известная как монеты конфиденциальности) может скрывать источник, место назначения и сумму средств в транзакциях, используя конфиденциальные транзакции. Такие криптовалюты по умолчанию более закрыты, но и они не гарантируют полную защиту от деанонимизации.
Является ли криптовалюта ценной?
В традиционных финансовых системах ценность валюты является общепринятым понятием. В случае криптовалюты её ценность определяется сообществом – по аналогии с ценными вещами. Другими словами, предмет имеет ценность, если люди верят в это. Данное утверждение верно независимо от того, является ли данный объект ценности драгоценным металлом, листом бумаги или файлом в базе данных.
Некоторые также рассматривают криптовалюты и биткоин как некий дефицитный цифровой товар. Из-за предсказуемости его эмиссии и денежно-кредитной политики считается, что в будущем биткоин может использоваться как средство сбережения, подобно золоту. Но поскольку биткоин существует пока немногим более десяти лет, нам еще предстоит увидеть, пройдет ли он проверку временем.
Являются ли все виды цифровых валют криптовалютами?
Вовсе нет. Вероятно, вы уже знаете о том, что многие государственные банки работают над созданием собственных цифровых валют. Но это не что иное, как цифровая версия обычных денег. Их также часто называют цифровыми валютами центрального банка (CBDC). По сути, это цифровые версии фиатных денег, не обладающие большей частью преимуществ криптовалют. Их выпускает и объявляет законным платежным средством центральное правительство, и обычно такая валюта не использует распределенный реестр типа блокчейна для учета транзакций.
Возможно, вы также слышали о Facebook Libra, еще одном виде цифровой валюты. Ее достоинство заключается в том, что она будет построена на блокчейн-системе с открытым исходным кодом. Однако она не будет общедоступной (как, например, биткоин или эфириум), а значит, пользователям будет недостаточно одного лишь подключения к интернету, чтобы ее использовать. Более того, деятельность проекта будет регулироваться ассоциацией, состоящей из нескольких выбранных участников.
Таким образом, несмотря на существование CBDC и других цифровых денег, использующих блокчейн или криптографию, они существенно отличаются от биткоина и других криптовалют.
Что такое рыночная капитализация криптовалюты?
Актуальная цена криптовалюты – это лишь часть общей картины. Не менее важным показателем является количество существующих единиц этой криптовалюты, то есть общий объем монет.
В частности, чтобы оценить стоимость криптовалютной сети, вам необходимо знать, сколько отдельных единиц существует в настоящий момент. Это называется количеством в обращении, или циркулирующим предложением. Разные криптовалюты могут иметь разные графики выпуска монет, поэтому важно учитывать, как эмиссия работает с каждой сетью.
Рыночная капитализация (от англ. market capitalization, market cap) – это цена отдельной единицы, умноженная на циркулирующее предложение.
рыночная капитализация = циркулирующее предложение * цена актива
Таким образом, рыночная капитализация криптовалютной сети является более точным представлением о её стоимости, чем цена отдельной криптоединицы. Сеть с дешевой монетой, но высоким циркулирующим предложением может иметь более высокую общую стоимость (рыночную капитализацию), чем сеть с дорогой монетой, но более низким циркулирующим предложением. В отдельных случаях возможна и полностью противоположная ситуация.
Однако стоит учитывать то, что рыночная капитализация не отражает общее число денег, поступивших на конкретный рынок. Например, среди новичков распространено заблуждение, что рыночная капитализация биткоина представляет собой общую сумму денег, вложенных в первую криптовалюту, но данное утверждение не имеет смысла, потому что рыночная капитализация зависит от цены и предложения.
Почему я должен оплачивать комиссию за транзакции?
Если вы отправляете биткоины на другой адрес, получателю придет чуть меньше средств, чем вы отправляли. При переводе взимается небольшая комиссия в качестве награды для майнеров за добавление вашей транзакции в блокчейн.
Многие криптовалюты используют аналогичный механизм, чтобы мотивировать пользователей защищать сеть. В системах Proof of Work комиссии за транзакции обычно объединяются с недавно созданными монетами (награда за блок), из которых формируется вознаграждение.
Вы можете настроить сумму комиссии в зависимости от срочности вашей транзакции. Но учитывайте то, что рациональные майнеры всегда стремятся получать как можно более высокую прибыль, поэтому отдают предпочтение транзакциям с более высокой комиссией. Вам следует изучить текущие транзакции в режиме ожидания для того, чтобы получить общее представление о средней комиссии и в соответствии с этим настроить свою собственную.
Я потерял свой ключ. Могу ли я вернуть свои средства?
Если вы абсолютно уверены в том, что потеряли свои ключи, то, вероятнее всего, никогда не получите их обратно. Большим преимуществом криптовалюты является исключение посредников из процесса управления финансовыми транзакциями. Вместе с тем одним из недостатков данной системы является то, что вся ответственность за управление средствами лежит на самом пользователе. Так что вы должны быть предельно осторожны, чтобы не потерять свои приватные ключи, поскольку именно они дают вам право собственности на ваши средства.
Какое будущее ждет криптовалюту?
На вопрос о будущем криптовалют каждый ответит по-разному. Некоторые считают, что биткоин заменит золото в цифровую эпоху, вытеснив существующую финансовую систему. Некоторые утверждают, что криптовалюты всегда будут вторичной системой, существующей как нишевый рынок. Есть и те, кто верит в то, что Ethereum станет распределенным компьютером – будущей основой нового интернета.
Скептики утверждают, что отрасль в конечном итоге рухнет. Энтузиасты были бы рады сохранить криптовалюту на уровне нишевой денежной системы. Рассуждений на тему будущего сегодня так много, что пока не представляется возможным давать точные прогнозы хотя бы на год. Но мы, безусловно, не можем отрицать исключительный потенциал криптоиндустрии и перспективы ее дальнейшего роста.